- Prerequisites
- Step 1. Provision device
- Step 2. Connect device
- Step 3. Create dashboard
- Step 4. Configure alarm rules
- Step 5. Create alarm
- Step 6. Alarm notifications
- Step 7. Assign device and dashboard to customer
- Next steps
- Your feedback
The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate the basic usage of the most popular ThingsBoard features. You will learn how to:
- Connect devices to ThingsBoard;
- Push data from devices to ThingsBoard;
- Build real-time end-user dashboards;
- Define thresholds and trigger alarms;
- Set up push notifications about new alarms over email, SMS, or other systems.
In this guide, we will connect and visualize data from the temperature sensor to keep it simple.
Prerequisites
You will need to have ThingsBoard server up and running. The easiest way is to use Live Demo server.
The alternative option is to install ThingsBoard using Installation Guide. Windows users should follow this guide. Linux users that have docker installed should execute the following commands:
1
2
3
4
mkdir -p ~/.mytb-data && sudo chown -R 799:799 ~/.mytb-data
mkdir -p ~/.mytb-logs && sudo chown -R 799:799 ~/.mytb-logs
docker run -it -p 8080:9090 -p 7070:7070 -p 1883:1883 -p 5683-5688:5683-5688/udp -v ~/.mytb-data:/data \
-v ~/.mytb-logs:/var/log/thingsboard --name mytb --restart always thingsboard/tb-postgres
These commands install ThingsBoard and load demo data and accounts.
ThingsBoard UI will be available using the URL: http://localhost:8080. You may use username [email protected] and password tenant. More info about demo accounts is available here.
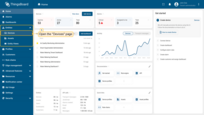
Step 1. Provision device
As an example, let’s add a device that will transmit the following data to ThingsBoard platform: the device’s name and temperature readings as telemetry.
To add a new device, follow these steps:
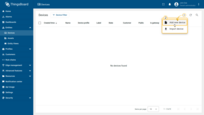
- Login to your ThingsBoard instance and go to the "Devices" page of the "Entities" section;
- Click on the "+" icon in the top right corner of the table and then select "Add new device" from drop-down menu;
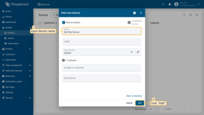
- Enter the device name. For example, "My New Device". No other changes required at this time. Click "Add";
- A window will open where you can check the device's connection to ThingsBoard. This step is optional. Let's close this window for now and return to checking the connection in the next step in more detail;
- Congratulations on adding your first device! As you add more devices, the will be added at the top of the table, since the table automatically sorts devices by their creation time, with the newest ones first.
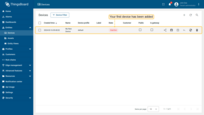
When adding a new device, you will receive a notification. You can view it by clicking on the “bell” icon in the top right corner.
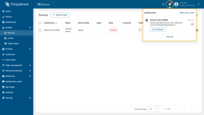
Learn more about notifications and how to configure them here.
You may also use:
- Bulk provisioning to provision multiple devices from a CSV file using UI;
- Device provisioning to allow device firmware to provision the device automatically, so you don’t need to configure each device manually;
- REST API to provision devices and other entities programmatically;
Step 2. Connect device
Now, let’s check the connection of our device to the ThingsBoard platform. To accomplish this, use the “Check connectivity” functionality to publish telemetry data (for example, temperature readings) on behalf of your device. You can do this both while adding the device and after.
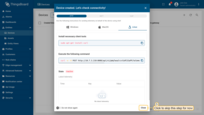
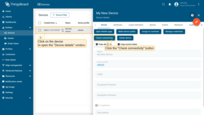
- Click on the your device, and click the "Check connectivity” button in the "Device details" window;
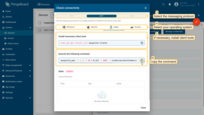
- In the opened window select the messaging protocol and your operating system. Install the necessary client tools and copy the command;
- Execute previously copied command. Once you have successfully published the “temperature” readings, the device state should be changed from "Inactive" to "Active" and you should see the published "temperature" readings. Now, close the connectivity window.
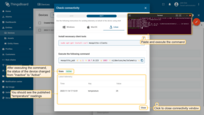
You may also use ThingsBoard API reference. Here, you can find more detailed information about all supported protocols for device connectivity.
Step 3. Create dashboard
A dashboard in ThingsBoard allows users to visualize and monitor data collected from IoT devices.
Let’s create a dashboard and add three widgets to it in order to display a list of entities and their latest values, as well as show alarm signals related to the specified entity.
Step 3.1 Create an empty dashboard
To create a new dashboard, follow these steps:
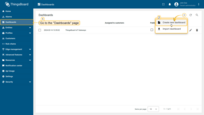
- Navigate to the "Dashboards" page through the main menu on the left of the screen. Then, click the "+" sign in the upper right corner of the screen, and select "Create new dashboard" from the drop-down menu;
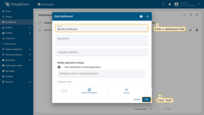
- In the opened dialog, it is necessary to enter a dashboard title, description is optional. Click "Add";
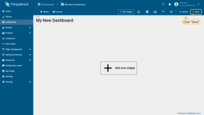
- After creating the dashboard, it will open automatically, and you can immediately start adding widgets to it. To save the dashboard, click "Save" button in the upper right corner;
- Your first dashboard has been successfully created. As you continue to add new dashboards, they will appear at the top of the list. This default sorting is based on the creation timestamp.
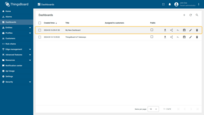
Step 3.2 Add an Entities table widget
The “Entities table” widget displays a list of entities and their latest values. The list of entities corresponds to selected devices or other entities, and filters with the ability of additional full-text search and pagination options.
To add the table widget we need to select it from the widget library. Widgets are grouped into widget bundles. Each widget has a data source. This is how the widget “knows” what data to display. To see the latest value of our “temperature” data that we sent during step 2, we should configure the data source.
Let’s add your first widget:
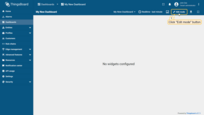
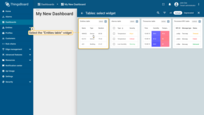
- Enter dashboard edit mode. Simply open the dashboard and click the "Edit mode" button found in the upper right corner of the screen;
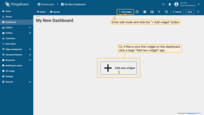
- Click the "Add widget" button at the top of the screen or click the large "Add new widget" icon in the center of the screen (if this is your first widget on this dashboard);
- Find the "Tables" widget bundle and click on it;
- Select the "Entities table" widget;
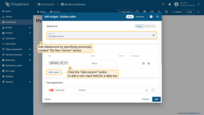
- The "Add Widget" window will appear. Specify the previously created device "My New Device" as the data source in the "Device" field. The "name" key has already been added to the "Columns" section, which is responsible for the column with the device name. You need to add another column that will display the value of the "temperature" key. To do this, click "Add column" to add a new field to enter the data key;
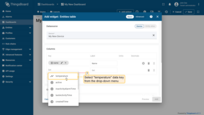
- Click on the newly appeared data key input field. A list of available data keys will open. Select "temperature" data key;
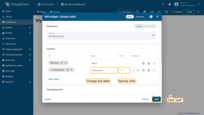
- Click the "Add" button in the bottom right corner of the widget to complete adding the widget.
- To make the widget slightly larger, simply grab the bottom right corner and drag it. Once you're happy with the new size, don't forget to click "Save" to save your changes to the dashboard.
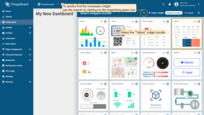
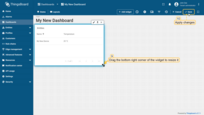
Congratulations! You’ve added your first widget.
In the “Entities table” widget, there are two columns. The first column displays the device’s name, and the second column displays the value of the “temperature” key (device telemetry). So, each column corresponds to an added key.
Now you are able to send a new telemetry reading (as in Step 1), and it will immediately appear in the table.
Step 3.3 Add a Chart widget
Chart widgets allow you to display time series data with customizable line charts and bar charts.
To add the chart widget we need to select it from the widget library. Chart widget displays multiple historical values of the same data key (“temperature” in our case). We should also configure the time window to use the chart widget.
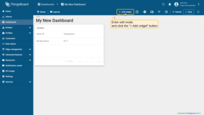
- Enter edit mode and click the "Add new widget" button at the top of the screen;
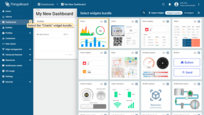
- Find the "Charts" widget bundle and click on it;
- Select the "Time series сhart" widget;
- Specify the previously created device "My New Device" as the data source in the "Device" field. In the "Series" section, specify the data key "temperature" to start monitoring the temperature values of the device. Then, click "Add";
- Resize the widget and apply changes. Publish different telemetry values multiple times, as in Step 2. Note that the widget displays only one minute of data by default. Click "Save" to apply changes;
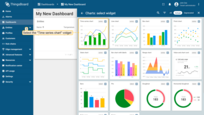
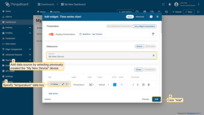
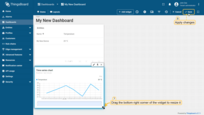
Congratulations! You have added the chart widget. Now you are able to send a new telemetry reading, and it will immediately appear in the chart.
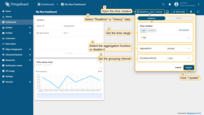
Also, you can open the timewindow and change the interval and aggregation function. Update the time window setting by clicking the “Update” button.
Step 3.4 Add an Alarms table widget
The alarms table widget displays alarms related to the specified entity in the certain time window. Alarm widget is configured by specifying an entity as the alarm source, and the corresponding alarm fields.
- Enter edit mode and click the "Add new widget" button at the top of the screen;
- Find the "Alarm widgets" bundle and click on it;
- Select "Alarms table" widget;
- Specify the previously created device "My New Device" as the data source in the "Device" field. Next, we will configure the filters. All alarms have specific severity and statuses. Mark those you want to see in the widget. If none are marked, all alarms will be displayed regardless of their status or severity;
- Congratulations! You have added the alarm widget. By default, new widgets are added one below the other, stacking downwards. Let's organize our widgets a bit to tidy up their arrangement. Drag the "Time series chart" widget to the top right corner of the dashboard to make room for the "Alarms table" widget;
- Scroll down, find the "Alarms table" widget, and drag it over to a free spot. Adjust its size to fit your needs. After you're done tweaking, click "Save" to save the dashboard.
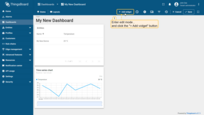
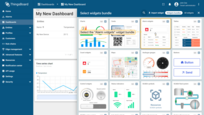
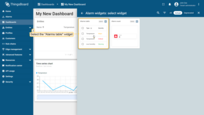
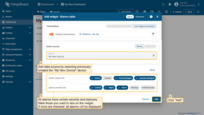
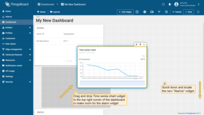
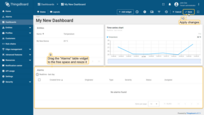
Now it’s time to configure alarm rules and raise some alarms.
Note: in this documentation, we are using a single device as a data source for the widgets. To use dynamic entities (for example, devices of a certain type or related to a certain asset) as data source, you should use the alias. Alias is a reference to a single entity or a group of entities that are used in the widgets. You may learn more about different aliases here.
Step 4. Configure alarm rules
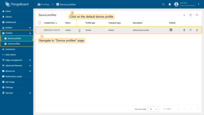
We will use the alarm rules feature to raise the alarm when the temperature reading is greater than 25 degrees. For this purpose, we should edit the device profile and add a new alarm rule. The “My New Device” is using the “Default” device profile. We recommend creating dedicated device profiles for each corresponding device type but will skip this step for simplicity.
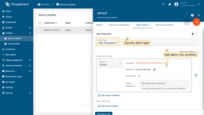
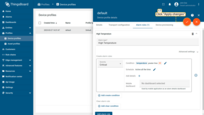
- Go to the "Device profiles" page of the "Profiles" section. Then click on the default device profile row to open its details;
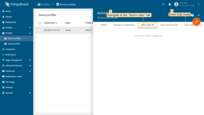
- Navigate to the "Alarm rules" tab and click "pencil" button to enter edit mode;
- Click "Add alarm rule" button;
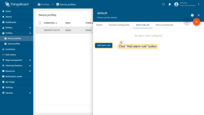
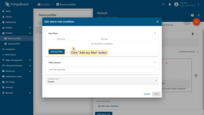
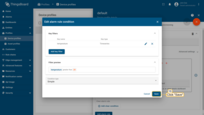
- Specify alarm type and click the "+" icon to add alarm rule condition;
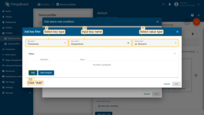
- Click the "Add key filter" button to specify a condition;
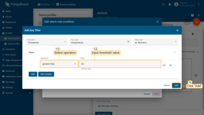
- Select a key type, enter a key name, and select a value type. Then, click "Add" button in the "Filters" section;
- Select an operation and enter a threshold value. Click "Add" button in the lower right corner;
- Click "Save";
- Finally, click "Apply changes".
Step 5. Create alarm
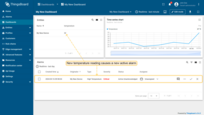
Now, our alarm rule is active (see Step 4), and we should send new telemetry on behalf of the device (see Step 2) to trigger the alarm. Note that the temperature value should be 26 or higher to raise the alarm. Once we send a new temperature reading, we should immediately see a new alarm on our dashboard.
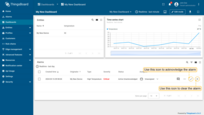
- Notice that the new temperature telemetry causes a new active alarm;
- You may acknowledge and clear alarms using the "Alarms table" widget;
- When you receive a new alarm, you will receive a message in the notification center. You can view the message by clicking on the bell icon in the upper right corner.
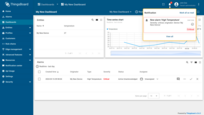
We also recommend reviewing alarm rule examples and documentation about alarm notifications.
Step 6. Alarm notifications
The ThingsBoard Notification center allows sending personalized notifications to end-users. These can include notifications about device activity, changes in temperature within your environment, or other events detected in your IoT ecosystem. Learn more about notifications and how to configure them here.
Additionally, the ThingsBoard Mobile Application allows users to receive instant push notifications directly on their smartphone. This ensures that you will always be timely informed about any events in your IoT solution, no matter where you are. Follow this guide to learn how to install the ThingsBoard PE Mobile Application and set up push notifications delivery directly from ThingsBoard instance to your smartphone.
Step 7. Assign device and dashboard to customer
One of the most important ThingsBoard features is the ability to assign Dashboards to Customers. You may assign different devices to different customers. Then, you may create a Dashboard(s) and assign it to multiple customers. Each customer user will see his own devices and will not be able to see devices or any other data that belongs to a different customer.
We have already created a Device (see Step 1), and a Dashboard (see Step 3). Now it’s time to create a Customer and a Customer User and make sure they will have access to the device’s data and the dashboard.
Step 7.1 Create customer
Let’s create a customer with the title “My New Customer”. Please see the instruction below:
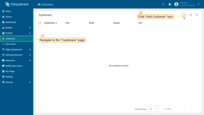
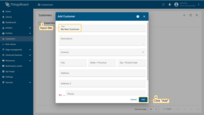
- Navigate to the Customers page. Click the "+" sign to add a customer;
- Input customer title and click "Add".
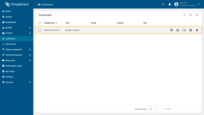
- The new customer has been created.
Step 7.2 Assign the device to customer
Let’s assign device to the customer. The customer users will have ability to read and write telemetry and send commands to devices.
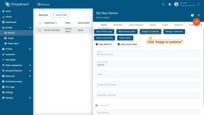
- Open "Devices" page, then select your device to open its details;
- Click "Assign to customer" button;
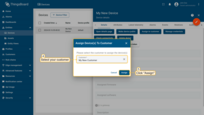
- Select the customer to whom you want to assign the device, and then click "Assign";
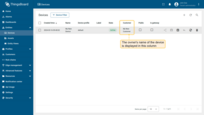
- You have changed the owner of the device. In the "Customer" column, you can see the owners name of the device;
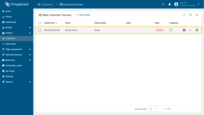
Make sure that the device is assigned to your customer.
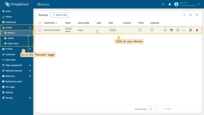
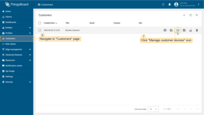
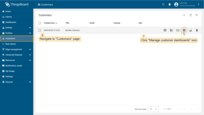
- Navigate to "Customers" page to make sure that the device is assigned to your customer. Find your customer in the list of customers and then click on the "Manage customer devices" icon;
- The device is with your client.
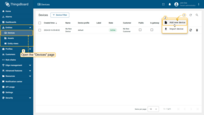
You can make the customer the owner of the device during its creation stage.
- Click on the "+" icon in the top right corner of the table and then select "Add new device" from drop-down menu;
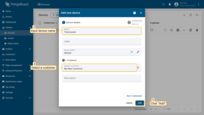
- Input device name (for example, "Thermostat") and select the customer in the "Assign to customer" field to whom you want to assign the new device. Then, click "Add";
- Close check connectivity window;
- The device has been created, and it immediately belongs to the selected customer.
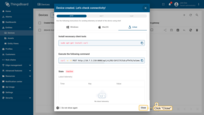
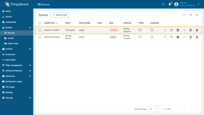
Step 7.3 Assign the dashboard to customer
Let’s share our dashboard with the customer. The customer users will have read-only access to the dashboard.
- Open "Dashboards" page. Mark your dashboard and click the "Assign dashboards" icon;
- Mark "My New Customer" and click "Assign";
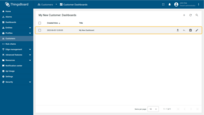
- Navigate to the "Customers" page. Click "Manage customer dashboards" icon for "My New Customer";
- "My New Dashboard" is assigned to your customer.
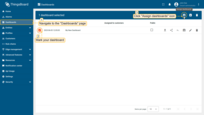
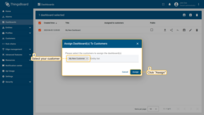
Step 7.4 Create customer user
Finally, let’s create a user that will belong to the customer and will have read-only access to the dashboard and the device.
You may optionally configure the dashboard to appear just after user login to the platform web UI.
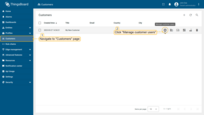
- Navigate to "Customers" page. Find your customer in the list of customers and then click on the "Manage customer users" icon;
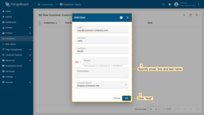
- Click the "Add user" icon in the top right corner of the table;
- Specify email that you will use to login as a customer user and click "Add";
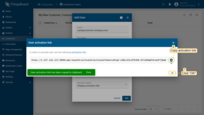
- Copy the activation link and save it to a safe place. You will use it later to set the password. Click "OK";
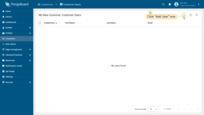
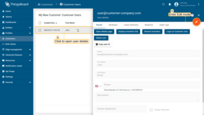
- Click on the created user to open details. Click "pencil" icon to enter edit mode;
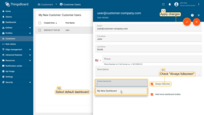
- Select your "My New Dashboard" as default dashboard and check "Always fullscreen". Apply changes.
Step 7.5 Activate customer user
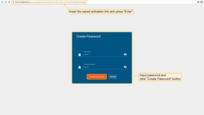
- Paste the previously copied link into a new browser tab and press Enter. Come up with and enter a password twice, then press "Create Password". You will automatically log in as a customer user;
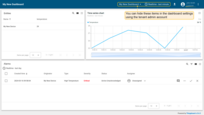
- You have logged in as a Customer User. You may browse the data and acknowledge/clear alarms.
Next steps
-
Connect your device - Learn how to connect devices based on your connectivity technology or solution.
-
Data visualization - These guides contain instructions on how to configure complex ThingsBoard dashboards.
-
Data processing & actions - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Rule Engine.
-
IoT Data analytics - Learn how to use rule engine to perform basic analytics tasks.
-
Hardware samples - Learn how to connect various hardware platforms to ThingsBoard.
-
Advanced features - Learn about advanced ThingsBoard features.
-
Contribution and Development - Learn about contribution and development in ThingsBoard.
Your feedback
Don’t hesitate to star ThingsBoard on github to help us spread the word. If you have some questions about this sample - post it on the forum.