- Prerequisites
- Guided Installation Using ThingsBoard Server Pre-configured Instructions
- Manual Installation and Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Next Steps
This guide will help you to install and start ThingsBoard Edge using Docker on Linux or Mac OS.
Prerequisites
To start utilizing the ThingsBoard Edge, it is essential to have an operational ThingsBoard server that supports Edge functionality.
The easiest way is to use Live Demo server.
Alternatively, you can install the ThingsBoard Community Edition server on-premise. For this, please refer to the ThingsBoard installation guide.
Edge Hardware Requirements
The hardware specifications needed for ThingsBoard Edge are determined by both the number of devices connected locally and the extent of GUI interaction:
-
Light Usage: If you intend to operate ThingsBoard Edge with minimal GUI interactions (such as local dashboards and device management) and anticipate connecting fewer than 100 devices to a single machine, a minimum of 1GB of RAM should suffice.
-
Heavy Usage: Conversely, for heavy GUI interactions and connections to 100+ devices on a single machine, we recommend allocating at least 4GB of RAM to ensure optimal performance.
Provisioning a new Edge instance on the ThingsBoard server
Additionally, you will need to provision Edge on the ThingsBoard server.
-
Sign in to your ThingsBoard instance and navigate to the “Edge Management” section -> “Instances” page. Click the “+” icon in the top right corner and select “Add new edge”.
-
Enter a name for your Edge. For instance, “My New Edge”. Click “Add” to confirm adding of your new Edge.
-
Your new Edge should now appear at the top of the list, as entries are sorted by creation time by default.
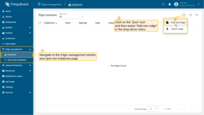
Sign in to your ThingsBoard instance and navigate to the “Edge Management” section -> “Instances” page. Click the “+” icon in the top right corner and select “Add new edge”.
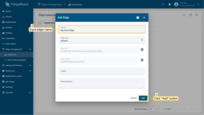
Enter a name for your Edge. For instance, “My New Edge”. Click “Add” to confirm adding of your new Edge.
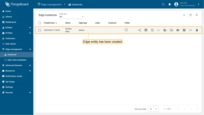
Your new Edge should now appear at the top of the list, as entries are sorted by creation time by default.
Docker installation
Guided Installation Using ThingsBoard Server Pre-configured Instructions
The most straightforward method to install and connect Edge to the Server is by utilizing the prepared installation instructions provided by the ThingsBoard Server. For every Edge Entity, the Server has prepared instructions with already populated fields such as the Edge secret key, Edge routing key, Edge RPC host URI, etc. Please follow the steps below to use these prepared instructions:
-
Click an Edge entity row to open it's details;
-
Click on the “Install & Connection Instructions” button;
-
Follow instructions to install Edge and connect to the server.
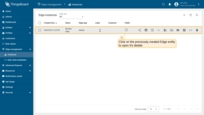
Click an Edge entity row to open it's details;
Click on the “Install & Connection Instructions” button;
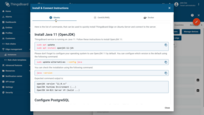
Follow instructions to install Edge and connect to the server.
Manual Installation and Configuration
If, for any reason, you are unable to use the prepared ThingsBoard Server Instructions above, please follow the generic steps outlined below. These steps will guide you through installing and configuring the Edge by yourself.
Step 1. Running ThingsBoard Edge
Here you can find ThingsBoard Edge docker image:
Click on Copy Edge Key and Copy Edge Secret in the edge details section. This will copy your edge credentials to your clipboard. Be sure to store them in a secure location, as these values will be needed in the following steps.
Create docker compose file for ThingsBoard Edge service:
1
nano docker-compose.yml
Add the following lines to the yml file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
version: '3.8'
services:
mytbedge:
restart: always
image: "thingsboard/tb-edge:3.8.0EDGE"
ports:
- "8080:8080"
- "1883:1883"
- "5683-5688:5683-5688/udp"
environment:
SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/tb-edge
CLOUD_ROUTING_KEY: PUT_YOUR_EDGE_KEY_HERE # e.g. 19ea7ee8-5e6d-e642-4f32-05440a529015
CLOUD_ROUTING_SECRET: PUT_YOUR_EDGE_SECRET_HERE # e.g. bztvkvfqsye7omv9uxlp
CLOUD_RPC_HOST: PUT_YOUR_CLOUD_IP # e.g. 192.168.1.1 or demo.thingsboard.io
volumes:
- tb-edge-data:/data
- tb-edge-logs:/var/log/tb-edge
postgres:
restart: always
image: "postgres:15"
ports:
- "5432"
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: tb-edge
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
volumes:
- tb-edge-postgres-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
tb-edge-data:
name: tb-edge-data
tb-edge-logs:
name: tb-edge-logs
tb-edge-postgres-data:
name: tb-edge-postgres-data
Where:
restart: always- automatically start ThingsBoard Edge in case of system reboot and restart in case of failure;8080:8080- connect local port 8080 to exposed internal HTTP port 8080;1883:1883- connect local port 1883 to exposed internal MQTT port 1883;-
5683-5688:5683-5688/udp- connect local UDP ports 5683-5688 to exposed internal COAP and LwM2M ports; -
thingsboard/tb-edge:3.8.0EDGE- docker image; CLOUD_ROUTING_KEY- your edge key;CLOUD_ROUTING_SECRET- your edge secret;CLOUD_RPC_HOST- ip address of the machine with the ThingsBoard platform;
Set the terminal in the directory which contains the docker-compose.yml file and execute the following commands to up this docker compose directly:
1
2
docker compose up -d
docker compose logs -f mytbedge
Step 2. Open ThingsBoard Edge UI
Once started, you will be able to open ThingsBoard Edge UI using the following link http://localhost:8080.
Please use your tenant credentials from local Server instance or ThingsBoard Live Demo to log in to the ThingsBoard Edge.
Step 3. Detaching, stop and start commands
You can detach from session terminal using Ctrl-p Ctrl-q key sequence - the container will keep running in the background.
In case of any issues you can examine service logs for errors. For example to see ThingsBoard Edge container logs execute the following command:
1
docker compose logs -f mytbedge
To stop the container:
1
docker compose stop mytbedge
To start the container:
1
docker compose start mytbedge
Troubleshooting
DNS issues
NOTE If you observe errors related to DNS issues, for example
1
127.0.1.1:53: cannot unmarshal DNS message
You may configure your system to use Google public DNS servers. See corresponding Linux and Mac OS instructions.
Next Steps
Congratulations! You have successfully provisioned, installed and connected ThingsBoard Edge to ThingsBoard server.
You can continue with Getting started guide to get the basic knowledge of ThingsBoard Edge or you can jump directly to more advanced topics:
-
Getting started guide - Provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard Edge features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes:
-
Edge Rule Engine:
-
Rule Chain Templates - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Edge Rule Chain Templates.
-
Provision Rule Chains from cloud to edge - Learn how to provision edge rule chains from cloud to edge.
-
- Security:
- gRPC over SSL/TLS - Learn how to configure gRPC over SSL/TLS for communication between edge and cloud.
-
Features:
-
Edge Status - Learn about Edge Status page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
Cloud Events - Learn about Cloud Events page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
-
Use cases:
-
Manage alarms and RPC requests on edge devices - This guide will show how to generate local alarms on the edge and send RPC requests to devices connected to edge:
-
Data filtering and traffic reduce - This guide will show how to send to cloud from edge only filterd amount of device data:
-
- Roadmap - ThingsBoard Edge roadmap.
