- Overview
- Configuration modes
- General settings
- Application
- Advanced application settings
- Data mapping
- Requests mapping
- EDE files parsing (Advanced configuration mode only)
- Advanced configuration
- Additional information
- Troubleshooting
- Next steps
Overview
This documentation will help you set up the BACnet connector for the ThingsBoard IoT Gateway. We’ll explain the configuration parameters in simple terms to make it easy for you to understand and follow. The BACnet protocol is widely used in building automation and control systems for applications such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting control, access control, and fire detection systems. Use general configuration to enable this extension.
The BACnet connector allows the ThingsBoard IoT Gateway to communicate with BACnet devices, enabling data exchange and control capabilities. The connector can be configured via the user interface form, which helps you set up a connection to the BACnet devices, collect data and write data to devices. Let’s look at all the available settings and explain each one clearly. This will help you understand how everything works.
Configuration modes
The BACnet connector can be configured in two modes: Basic and Advanced.
- Basic mode is designed for users who are new to ThingsBoard IoT Gateway and want to quickly set up the connector with minimal configuration. It provides a simplified interface with essential settings.
- Advanced mode is intended for experienced users who need more control over the configuration. It offers additional options and flexibility for advanced use cases.
You can switch between these modes using the toggle button at the top of the configuration page:
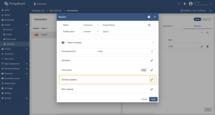
General settings
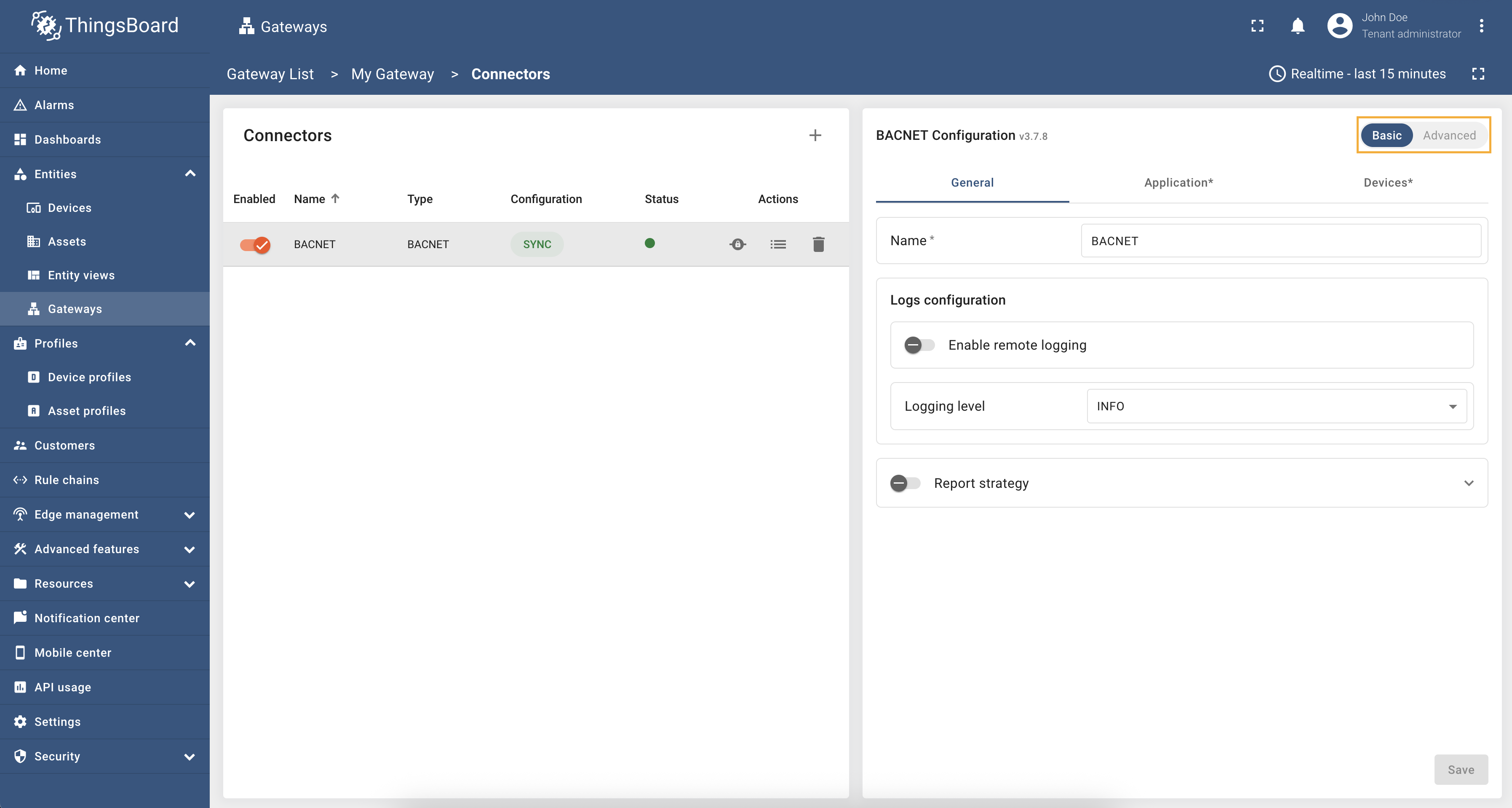
This configuration section contains general connector settings, such as:
- Name - connector name used for logs and saving to persistent devices;
- Logs configuration - settings for local and remote logging:
- Enable remote logging - enables remote logging for the connector;
- Logging level - logging level for local and remote logs: NONE, ERROR, CRITICAL, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE;
- Report strategy - strategy for sending data to ThingsBoard:
- Report period - period for sending data to ThingsBoard in milliseconds;
- Type - type of the report strategy:
- On report period - sends data to ThingsBoard after the report period;
- On value change - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes;
- On value change or report period - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes or after the report period;
- On received - sends data to ThingsBoard after receiving data from the device (default strategy).

Application
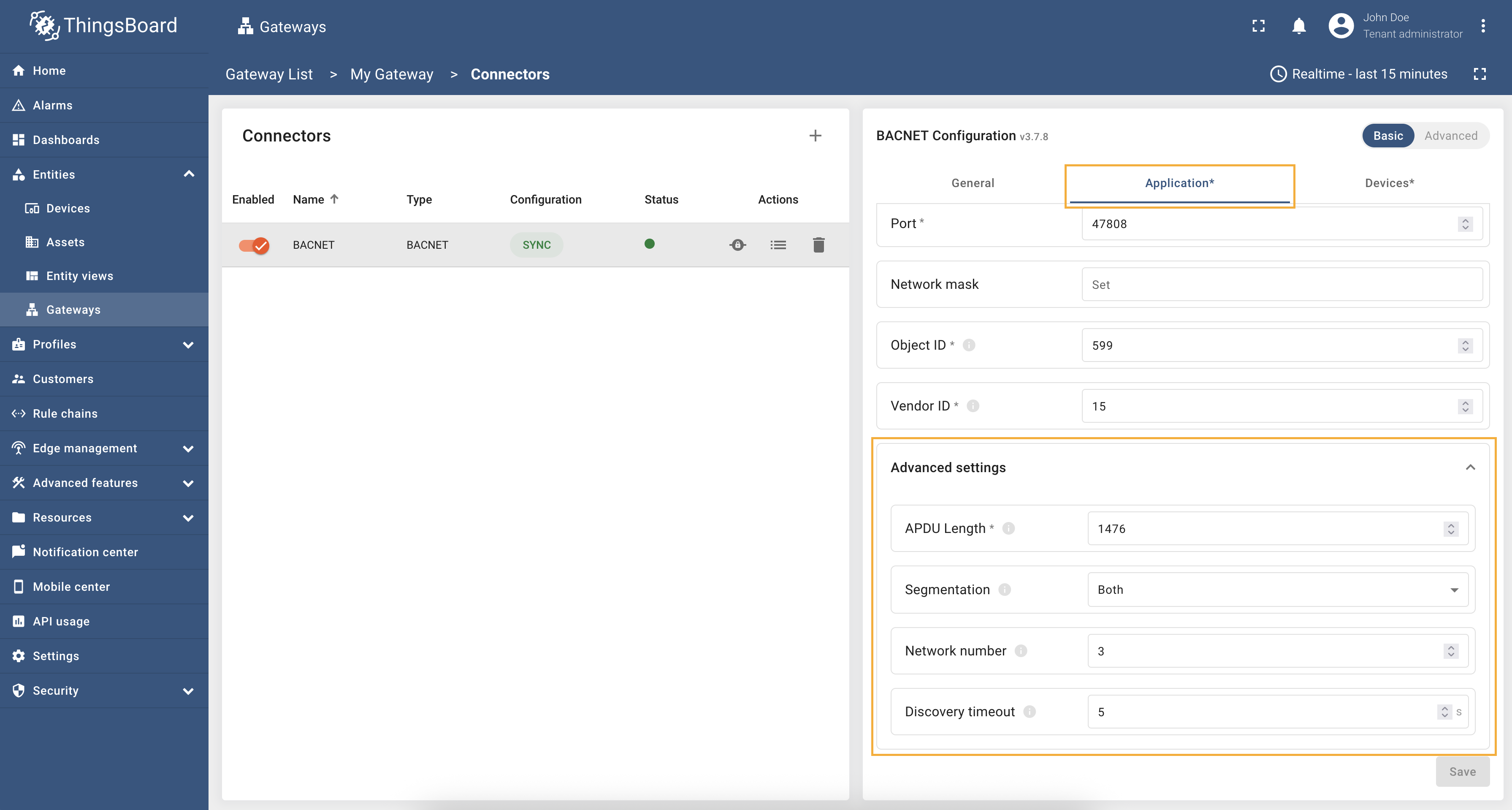
Configuration in this section is used to configure the gateway in the BACnet network. The following parameters are used to configure application settings:
- Object Name - the gateway object name in the BACnet network.
- Host - the gateway host in the BACnet network. Make sure you use the correct network address where your devices are located so that the gateway can find them.
- Port - the gateway port in the BACnet network.
- Network mask - the gateway mask in the BACnet network.
- Object ID - the gateway object identifier in the BACnet network.
- Vendor ID - the gateway vendor identifier in the BACnet network.

Advanced application settings
You can configure additional application settings like: APDU length, segmentation, network number and discovering timeout.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| APDU Length (in bytes) | 1476 | Maximal length of the APDU. |
| Segmentation | Both | Segmentation type for transmitting large BACnet messages. Can be: Both, Transmit, Receive, None. |
| Network number | 3 | Identifier of the network segment. |
| Discovering timeout (in sec) | 5 | Period of time when the connector will try to discover BACnet devices. |
Data mapping
This configuration section contains an array of BACnet devices that can be connected to the connector and send data. Any BACnet device not included in this array will be rejected by the connector.
To add a new device, click the “plus” icon:

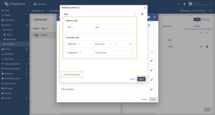
Provide the following fields in the opened model window:
- Host - the host of the device;
- Port - the port of the device;
- Device name source - the source of the device name, can be:
- Constant - the device name is static;
- Expression - the device name is an expression;
- Device name value / expression - the device name (you can find detail examples here);
- Device profile source - the source of the device profile, can be the same as the device name source;
- Device profile value / expression - the device profile name (you can find detail examples here);
- Poll period - the period of time when the connector will try to poll BACnet device;
- Advanced configuration settings:
- Alternative responses addresses - the alternative address for responses from the device (you can find detail examples here).
- Report strategy - strategy for sending data to ThingsBoard:
- Report period - period for sending data to ThingsBoard in milliseconds;
- Type - type of the report strategy:
- On report period - sends data to ThingsBoard after the report period;
- On value change - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes;
- On value change or report period - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes or after the report period;
- On received - sends data to ThingsBoard after receiving data from the device (default strategy).

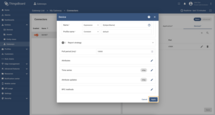
Attributes and Time series
This configuration section includes the parameters for handling incoming data. You can specify which data will be treated as device attributes and which as time series. Attributes are used for storing static or infrequently changing data, while time series are used for storing dynamic or frequently changing data.
Configuration in this subsection provides settings for processing data from BACnet device as timeseries and attributes on the platform instance.
To add new time series or attribute key, follow these steps:
-
Click “pencil” icon of the “Attributes” section to add new attribute key;
-
Click “Add attribute” in the opened window;
-
Enter the key name, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply”;
-
Now click on the “pencil” icon of the “Time series” section to add new time series key;
-
Click “Add time series” in the opened window;
-
Enter the key name, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply”.

Click “pencil” icon of the “Attributes” section to add new attribute key;

Click “Add attribute” in the opened window;

Enter the key name, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply”;

Now click on the “pencil” icon of the “Time series” section to add new time series key;

Click “Add time series” in the opened window;

Enter the key name, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply”.
Filtering (from v.3.7.5 and only in advanced configuration mode)
You can set up filtering for time series and attributes based on Object Type, Object ID and Property ID. This allows you to specify which data should be collected and sent to the platform. Let’s review each filtering option:
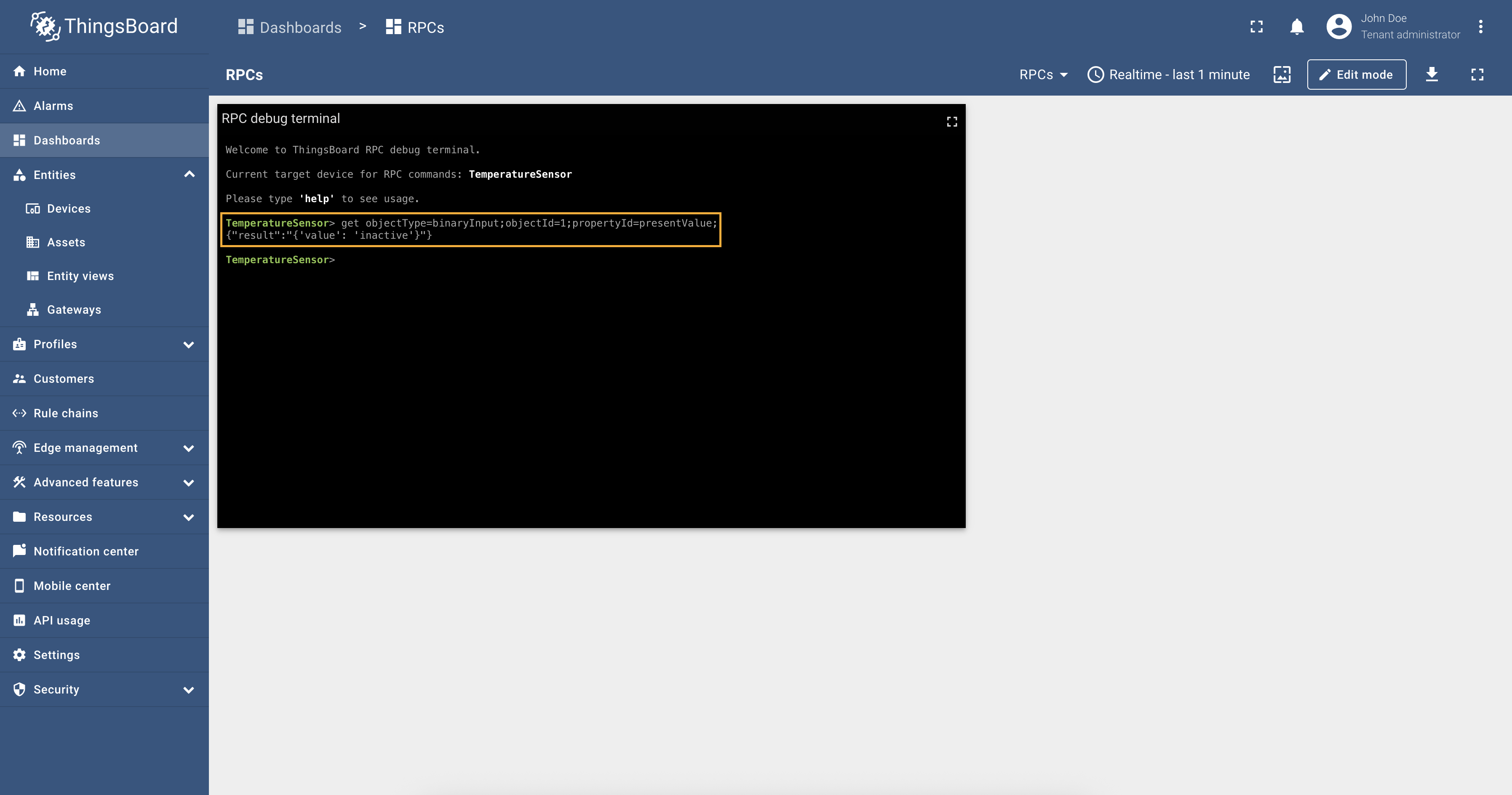
Object Type Filtering
This filter allows you to specify the type of BACnet objects from which data should be collected. For example, you can choose to collect data only from “Analog Input” or “Binary Output” object types or both:
"objectType": "*"- will collect data from all supported object types;"objectType": "analogValue"- will collect data only from Analog Value objects;"objectType": ["analogValue", "binaryInput"]- will collect data from both “Analog Value” and “Binary Input” objects.
Object ID Filtering
This filter allows you to specify particular Object IDs for data collection. You can define a single Object ID or a list of Object IDs:
"objectId": 1234- will collect data only from the object with ID 1234;"objectId": "*"- will collect data from all Object IDs;"objectId": "0-10"- will collect data from Object IDs in the range 0 to 10 (inclusive);"objectId": ["0-10", "12-15"]- will collect data from Object IDs in the ranges 0 to 10 and 12 to 15 (inclusive).
Property ID Filtering
This filter allows you to specify particular Property IDs for data collection. You can define a single Property ID or a list of Property IDs:
"propertyId": "presentValue"- will read only the “presentValue” property;"propertyId": "*"- will read all supported properties;"propertyId": ["presentValue", "location"]- will read both “presentValue” and “location” properties.
Example of filtering configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"timeseries": [
{
"key": "${objectName} - ${objectType} | ${units}",
"objectType": "analogInput",
"objectId": "*",
"propertyId": ["presentValue", "statusFlags"]
}
]
}
Report strategy
For each time series or attribute, you can enable specific report strategy. This strategy defines how often the data will be sent to the ThingsBoard server. The following strategies are available:
- On report period - sends data to ThingsBoard after the report period;
- On value change - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes;
- On value change or report period - sends data to ThingsBoard when the value changes or after the report period;
- On received - sends data to ThingsBoard after receiving data from the device (default strategy).

Usage examples
BACnet connector allows you to set dynamic device names and profiles using expressions. This is especially useful when
you have multiple devices with similar configurations and want to differentiate them based on their properties.
In this example, we will configure a BACnet device to have a dynamic device name based on its Here is an example configuration snippet for a BACnet device with dynamic device name and profile: In this configuration:
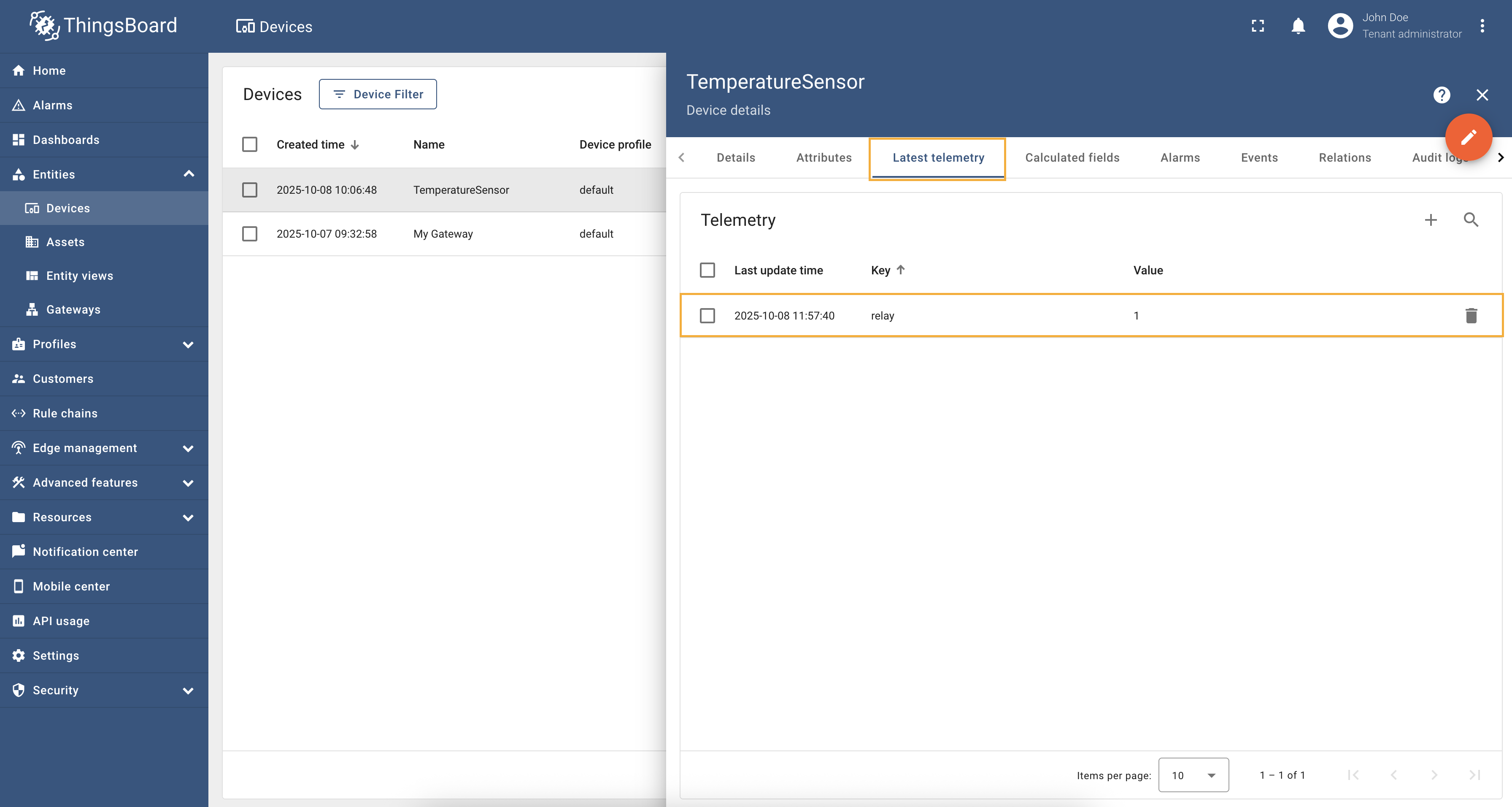
After applying this configuration, the device will be created with a name and profile that reflect its specific properties. The screenshot below shows how the device appears in ThingsBoard with the dynamic name and profile:
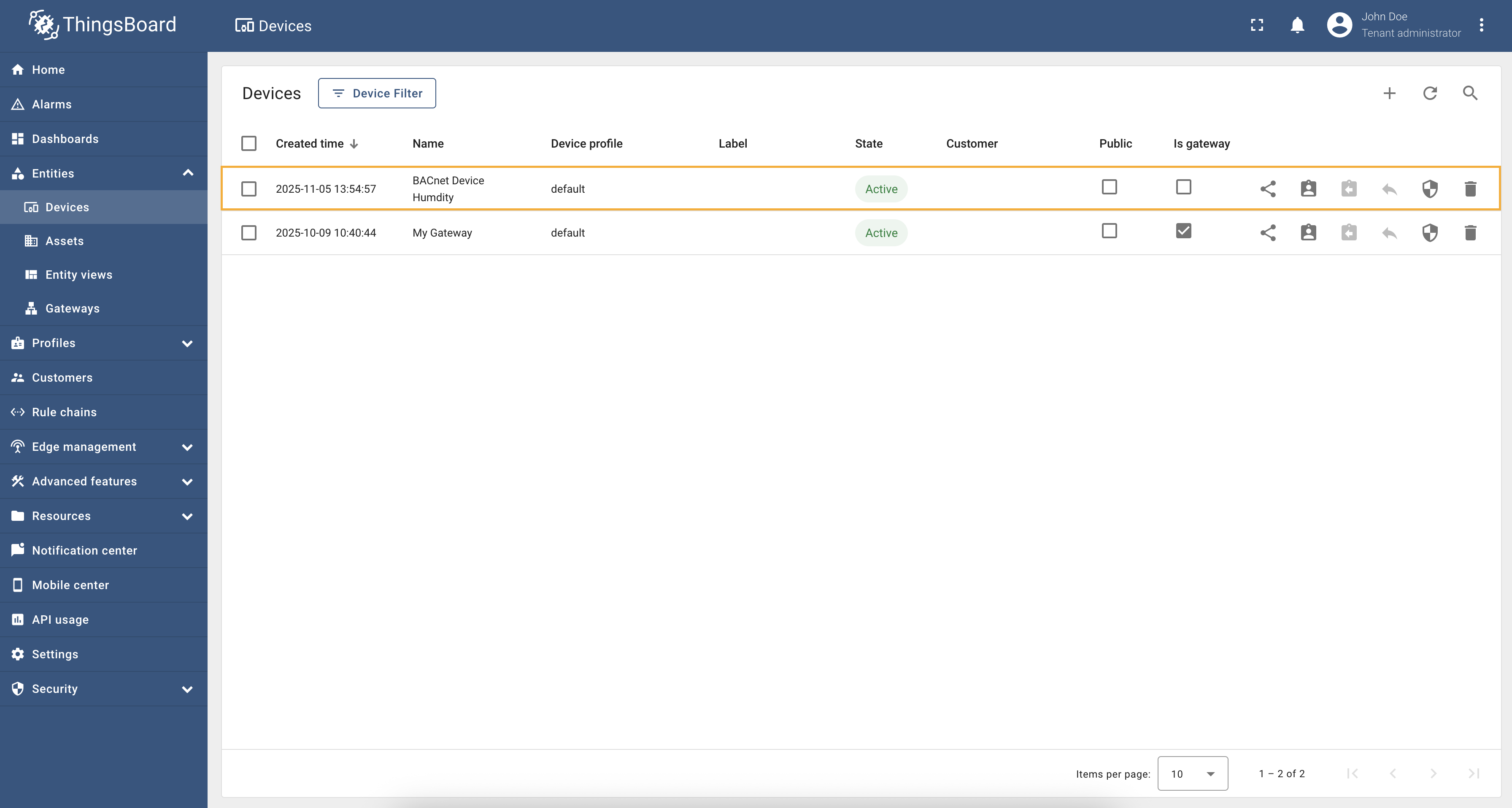
As you can see, the device name is generated based on the Device name/profile dynamic expressions provide flexibility in managing multiple BACnet devices with varying configurations and can help in organizing devices effectively within ThingsBoard. |
Alternative response addresses field allows you to specify an alternative IP address for device responses. It is especially useful when the gateway and the BACnet device are located in different networks. For example, consider the following network setup:
In this setup, the gateway runs inside a Docker container and the BACnet device is located on a local network with IP
address To configure the alternative response address, you need to add the After applying this configuration, the connector will use the specified alternative response address
|
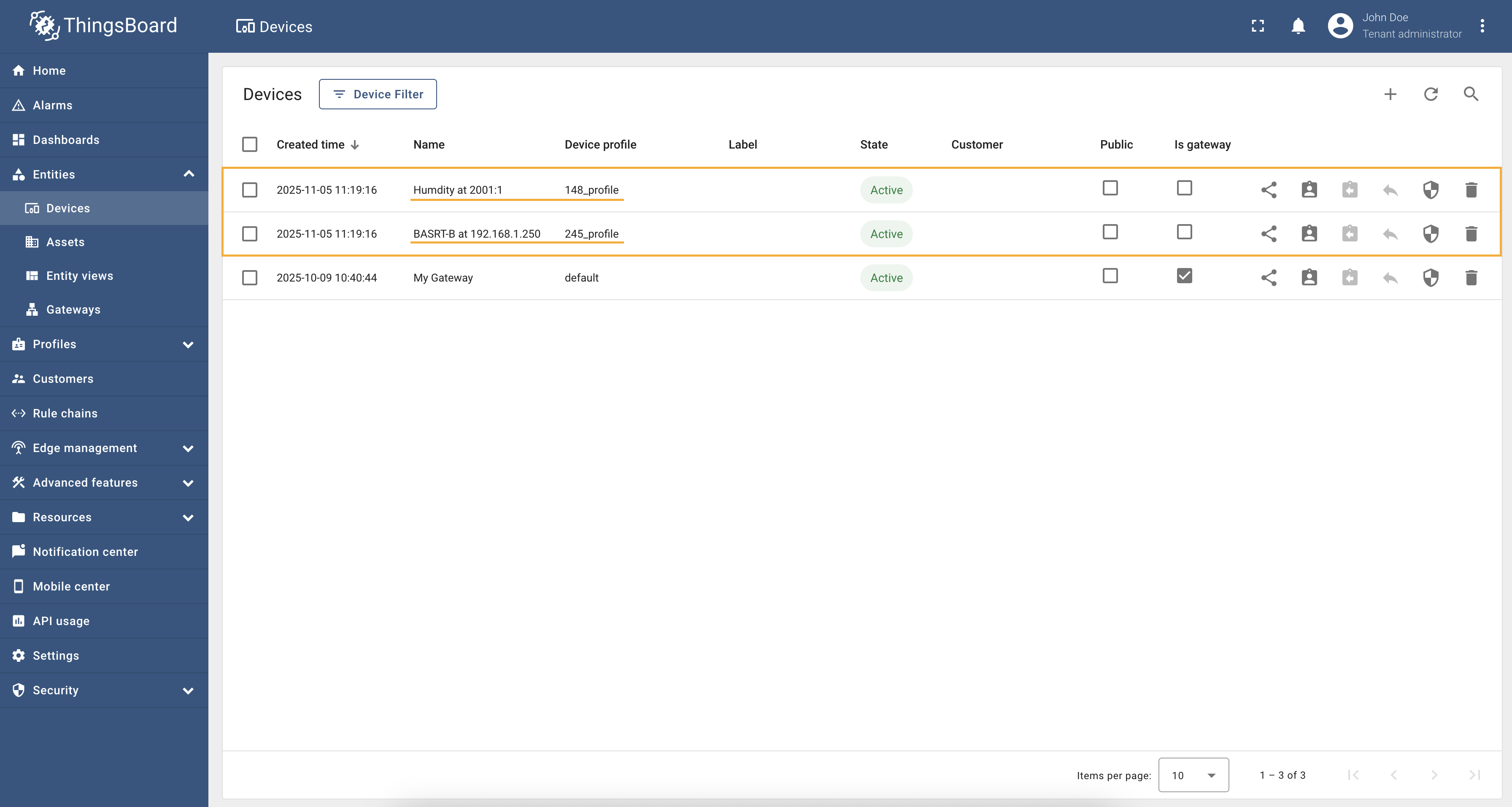
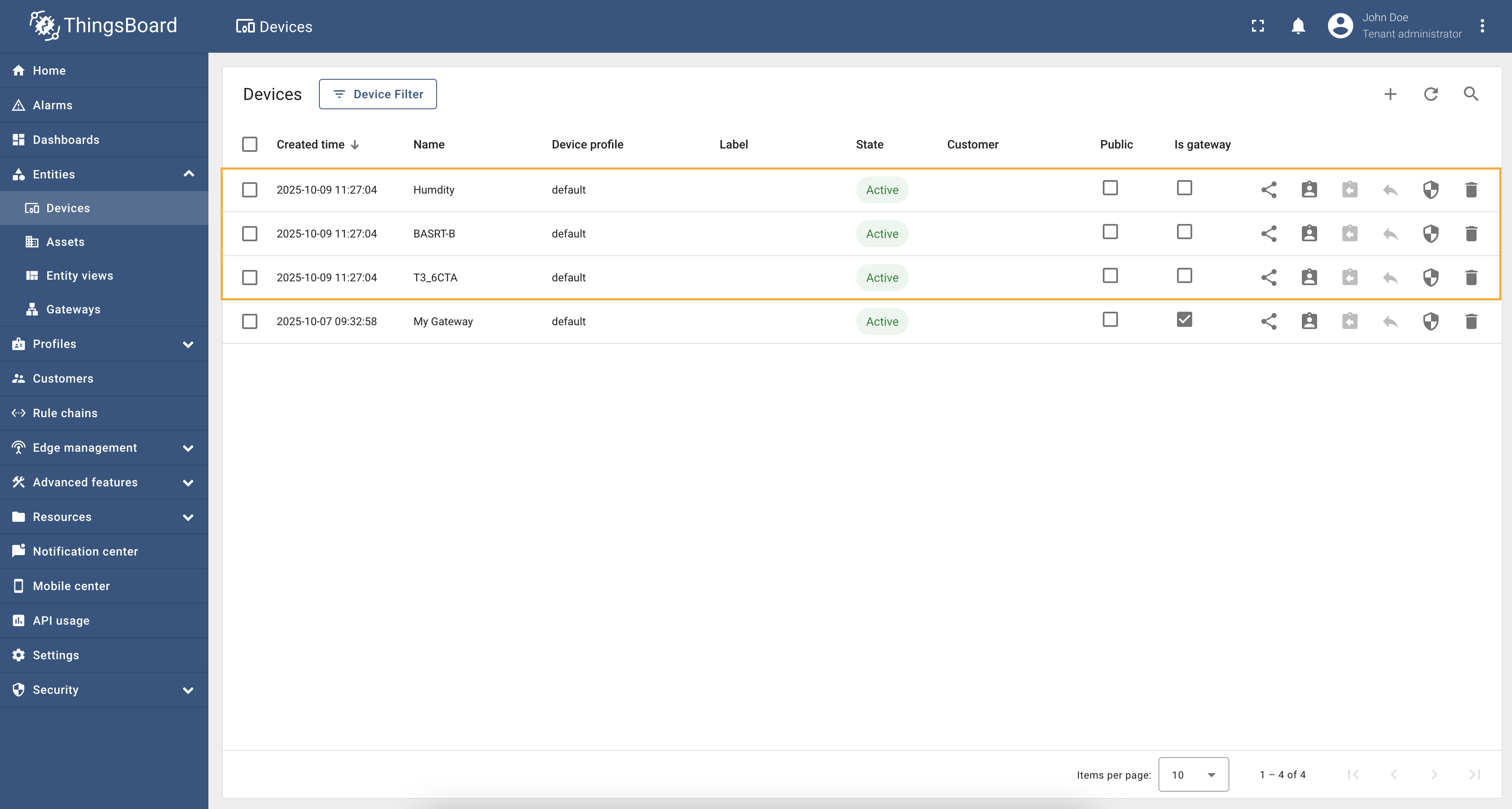
There are situations when there are many devices with the same list of objects, the values of which need to be read. Copying the configuration for each device is not very convenient, so the BACnet connector allows you to automatically find all devices on the network and connect them with the same configuration. To do this, you need to specify the host and port of the device, as well as set templates for the device name and device profile. Let’s look at an example of how to properly configure automatic device discovery. Suppose we have two devices with the same list of objects:
To configure automatic device discovery, use the following BACnet connector configuration: Below are the main parameters that you can use to properly configure automatic device detection. Let’s take a closer look at them:
After saving the changes and starting the connector, it will send a WhoIs query to the network and start receiving IAm messages from all devices. After receiving the IAm message, the connector will automatically create a device for each device found with the specified templates and start reading data from the objects. The screenshot below shows what the device list looks like after automatic discovery:
|
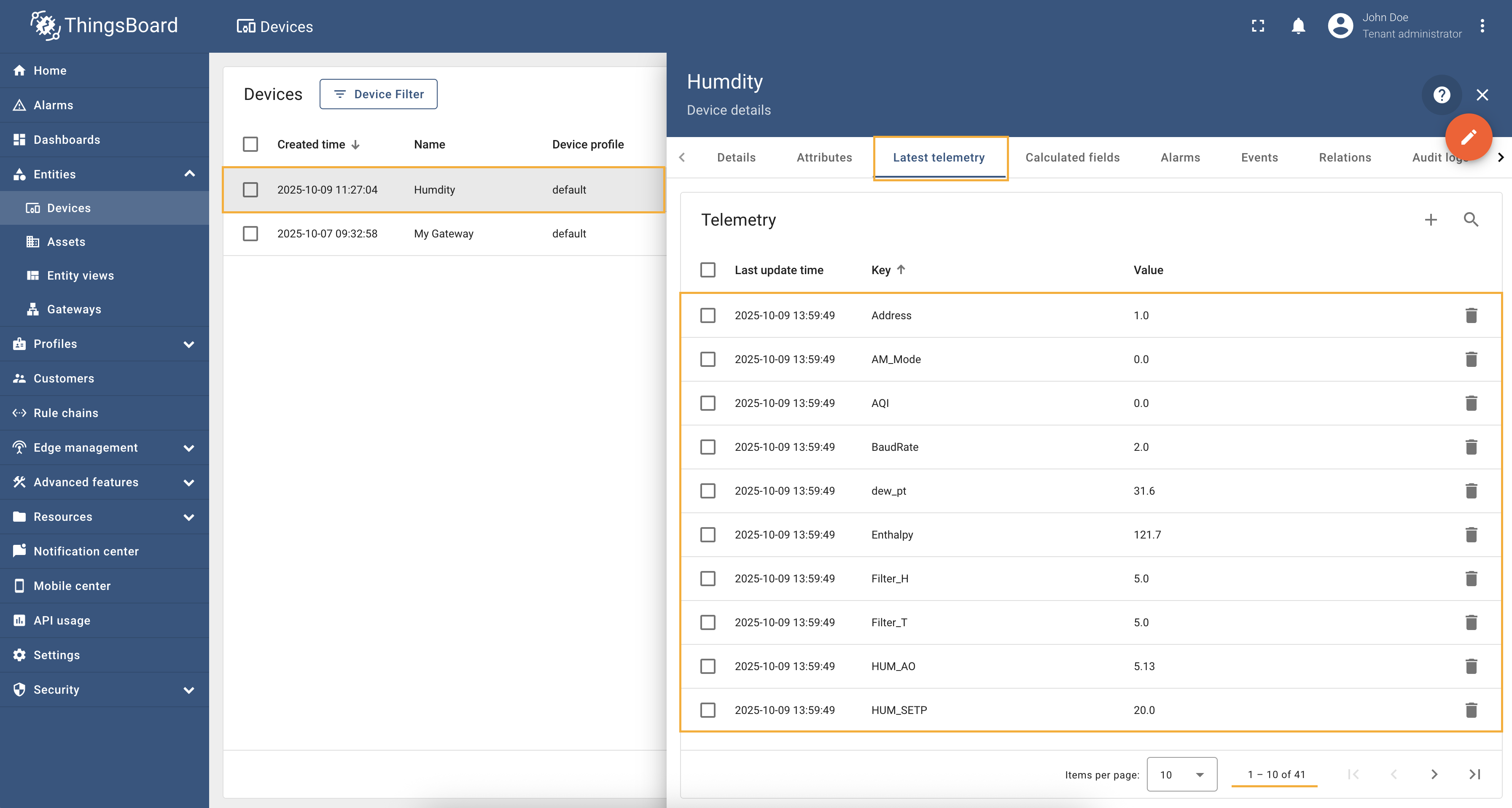
There are situations when a BACnet device has a lot of objects, and you want to read all the objects of the device without having to manually add each object to the connector configuration. Or maybe you don’t know what objects are in the device and want to read all the objects automatically. The BACnet connector supports this functionality and allows you to read all the objects of the device by easily configuring just one parameter. Let’s look at an example of how to properly configure reading all device objects. In order to read all the device objects, you need to decide where exactly the values of these objects will be stored:
in In our case, we will store all objects in time series, so the device configuration will look like this: As you can see from the configuration above, we have put After saving the changes and starting the connector, you can see that the corresponding device has been added to the platform, and its telemetry has started to fill with all the device objects:
|
There are situations when a BACnet device has a lot of objects, and you want to read only specific objects or properties from the device. You can use filtering options to specify which data should be collected and sent to the platform. Let’s look at an example of how to properly configure filtering feature. In our case, we have a device that have a lot of objects, but we want to read As you can see from the configuration above, we have specified After saving the changes and starting the connector, you can see that the corresponding device has been added to the platform, and its telemetry has started to fill with the filtered data. The screenshot below shows an example of how the device telemetry looks like after applying the filtering configuration:
|
Requests mapping
The Requests mapping section allows you to configure how the ThingsBoard platform instance will interact with the devices. That is, how the platform will request data from the devices, how it will update device attributes, and how it will send RPC commands to the devices.
BACnet connector supports the following requests mapping:
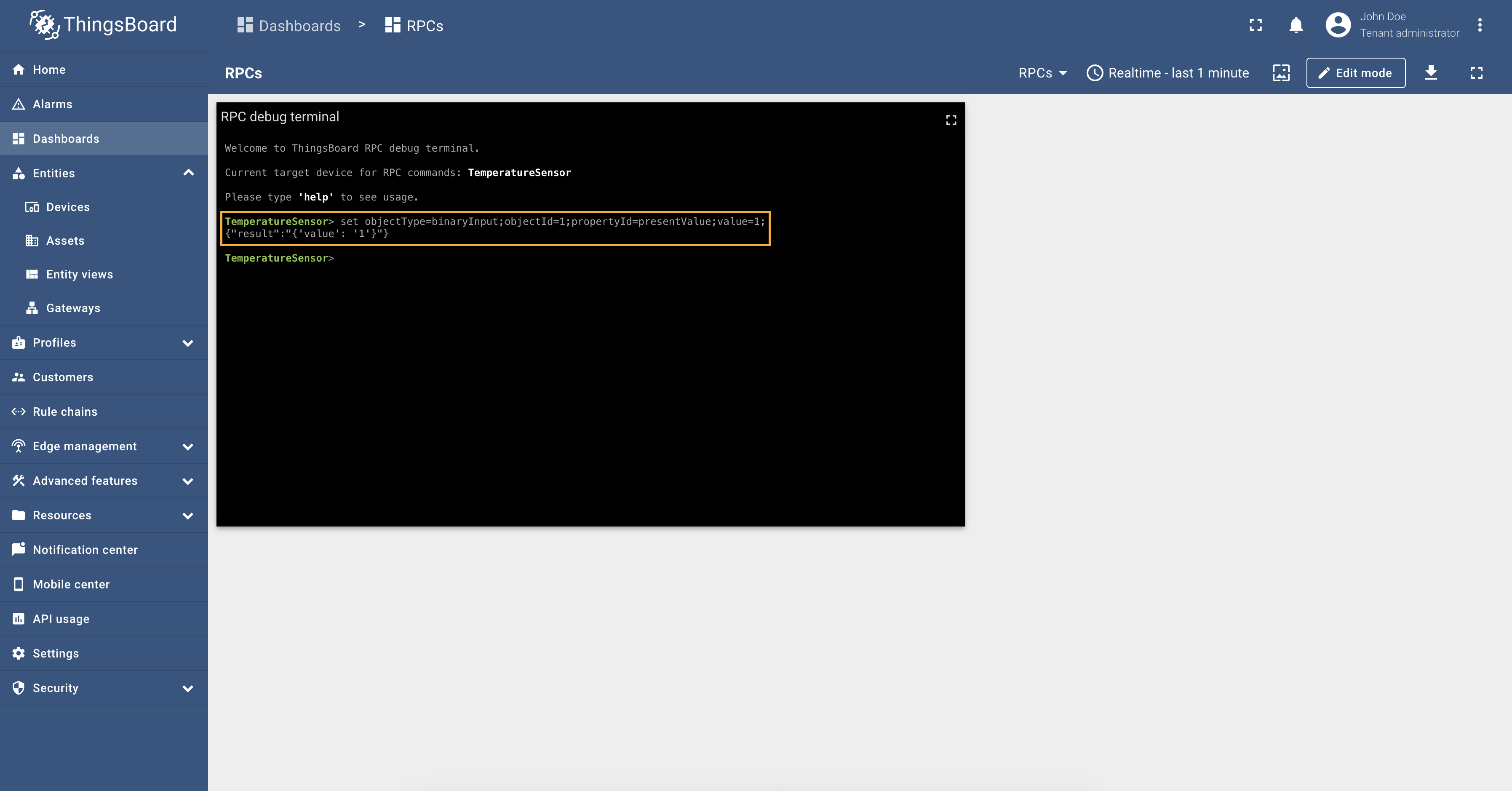
- Attribute updates - allows update device objects values from ThingsBoard platform instance.
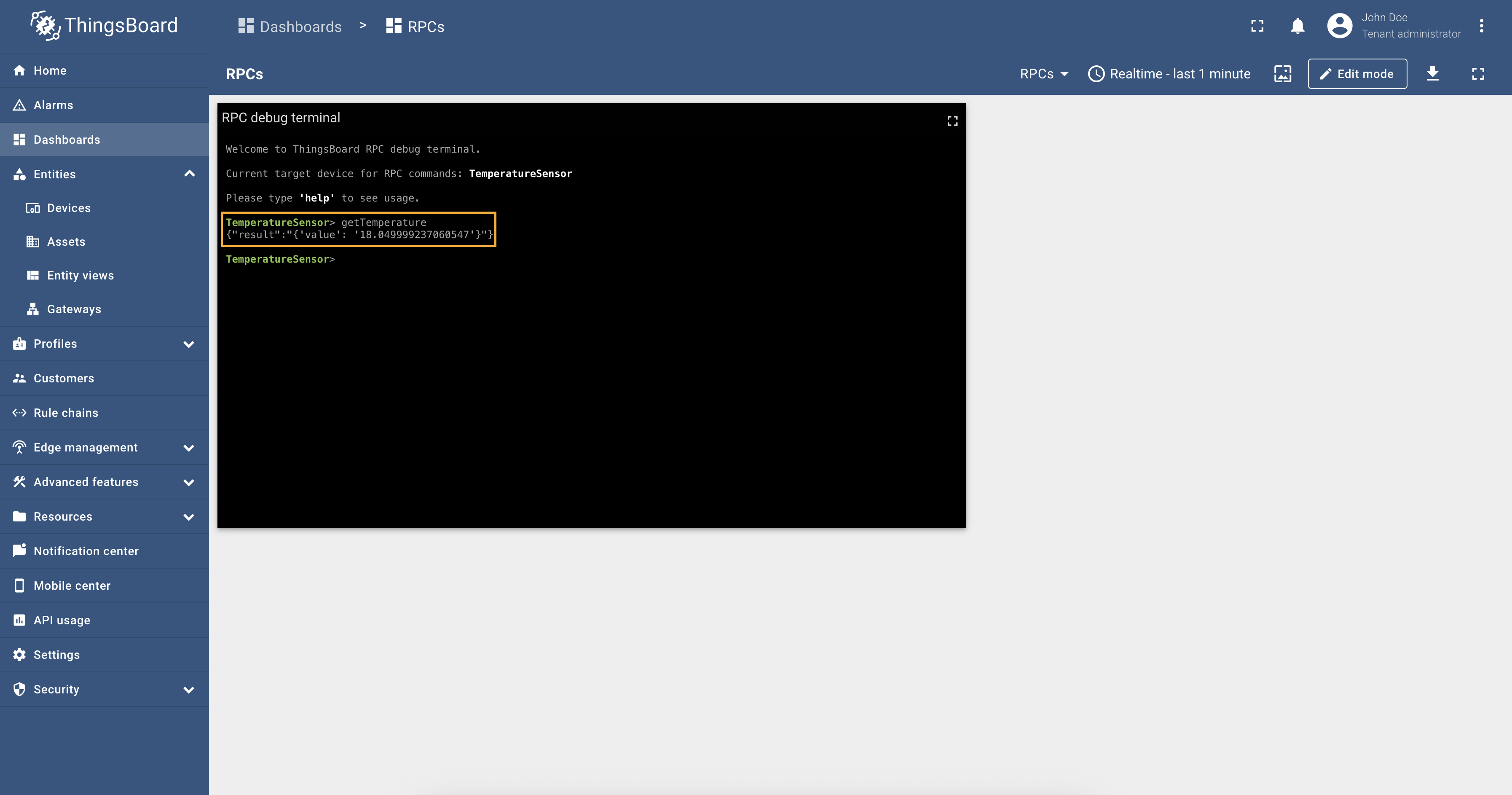
- RPC methods - allows sending RPC commands to devices. Using RPC methods, you can get or set values of the BACnet
device objects values. BACnet connector supports different types of RPC methods, such as:
- Reserved GET/SET methods - these methods are automatically created for each attribute and time series parameter. You can use them to get or set values of the BACnet device objects values.
- Configurable RPC to device - these methods allow you to configure custom RPC commands in connector configuration that can be sent to the devices.
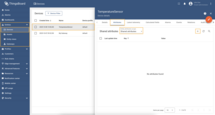
Attribute updates
This subsection contains configuration for attribute updates request from ThingsBoard platform instance.
ThingsBoard allows the provisioning of device attributes and fetches some of them from the device application. You can treat this as a remote configuration for devices, enabling them to request shared attributes from ThingsBoard. See user guide for more details.
The following parameters are used to configure attribute updates:
- Key - the key of the shared attribute in ThingsBoard. It can be specified as a static value.
- Object ID - the object id in the BACnet device.
- Object Type - the object type in the BACnet device.
- Property ID - the property id in the BACnet device.
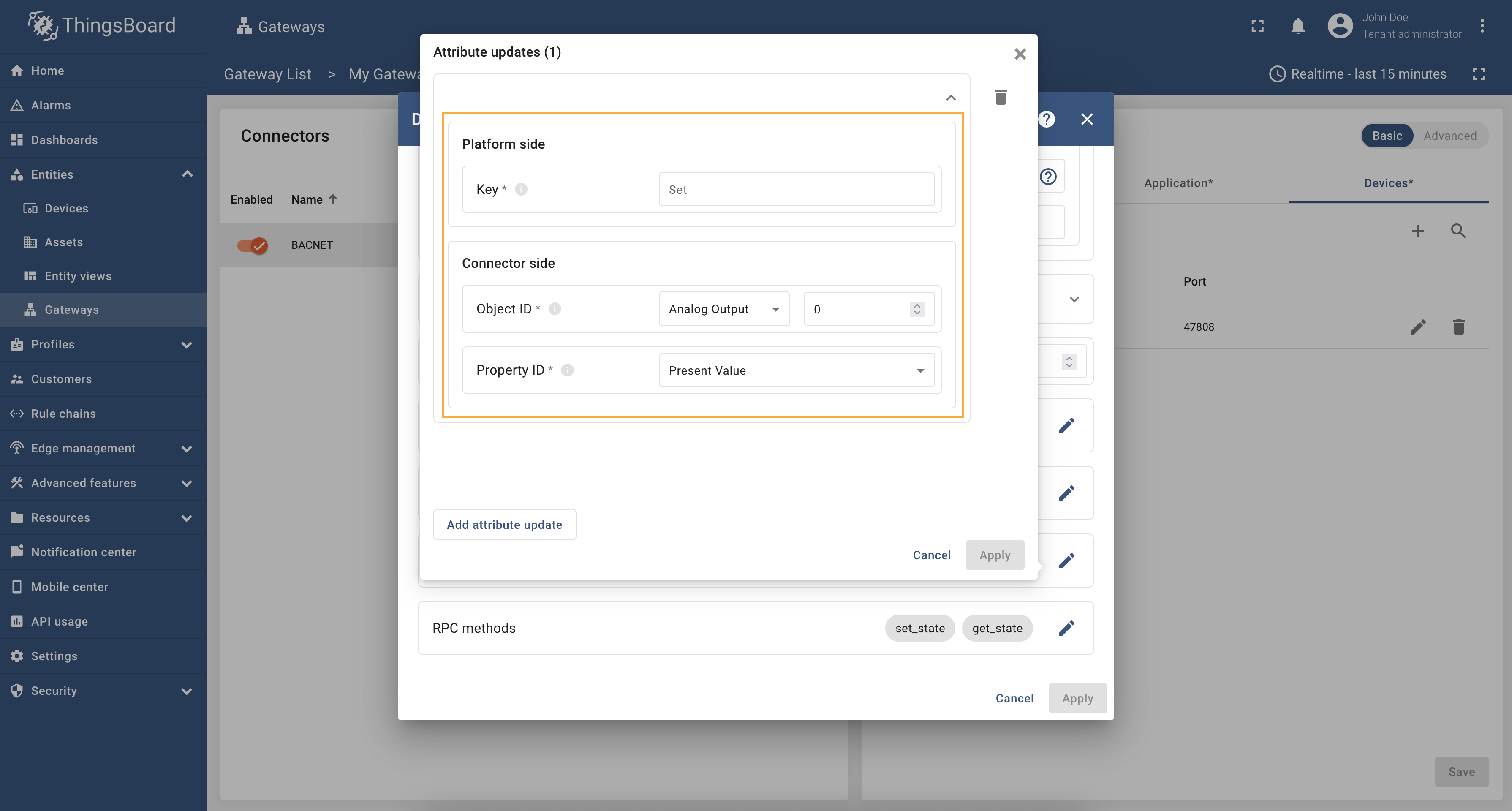
In order to add new attribute update, follow these steps:
-
Click “pencil” icon of the “Attribute updates” subsection to add new attribute update;
-
Click “Add attribute update” in the opened window;
-
Fill in “Key” field, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply” button.

Click “pencil” icon of the “Attribute updates” subsection to add new attribute update;

Click “Add attribute update” in the opened window;

Fill in “Key” field, select “Object ID” and “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply” button.
RPC methods
ThingsBoard allows sending RPC commands to devices connected directly to ThingsBoard or via Gateway. The following parameters are used to configure RPC methods:
- Method - the RPC method name.
- Request Type - “writeProperty” to write data and “readProperty” to read data.
- Object ID - the object id in the BACnet device.
- Object Type - the object type in the BACnet device.
- Property ID - the property id in the BACnet device.
- Request Timeout - timeout in milliseconds for the RPC method execution.
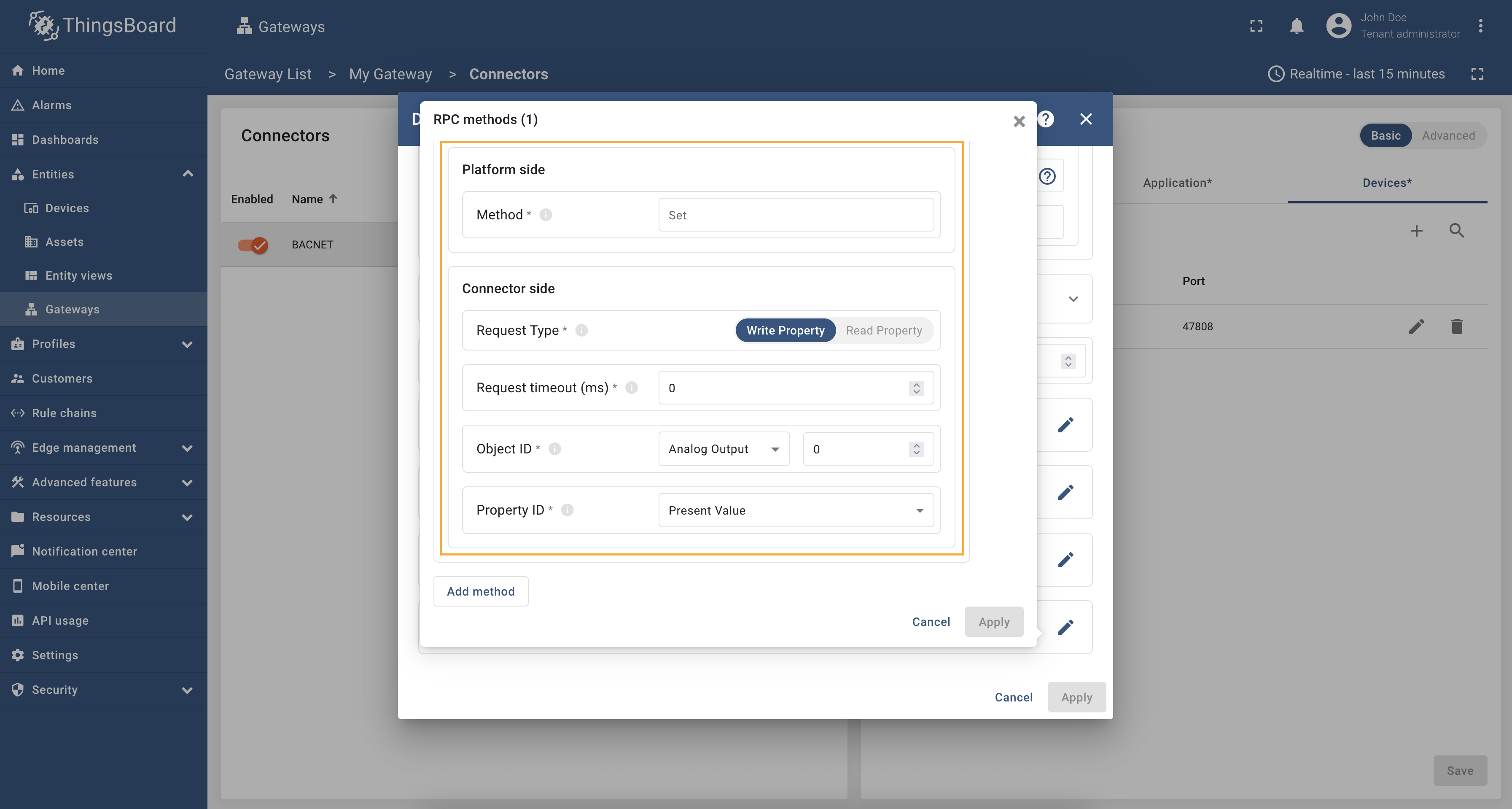
In order to add a new RPC method, follow these steps:
-
Click “pencil” icon of the “RPC methods” section to add new RPC;
-
In the opened window click “Add method”;
-
Fill in “Method” field, select “Request Type”, “Object ID”, “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply” button.

Click “pencil” icon of the “RPC methods” section to add new RPC;

In the opened window click “Add method”;

Fill in “Method” field, select “Request Type”, “Object ID”, “Property ID” from the dropdown list. Click “Apply” button.
Usage examples
EDE files parsing (Advanced configuration mode only)
The BACnet connector supports EDE files parsing. EDE (Engineering Data Exchange) files are used to describe the structure and properties of BACnet devices. By parsing EDE files, the BACnet connector can automatically configure itself to interact with the devices described in the files.
To use EDE files parsing, you need to provide the path to the EDE file in the connector configuration. The connector will then read the file and extract the necessary information to communicate with the BACnet devices. The EDE file should be in CSV format and follow the BACnet EDE schema.
Let’s look at the example of the EDE file parsing configuration.
We will use an EDE file exported from YABE (Yet Another BACnet Explorer) application. The file contains the description of a BACnet device with several objects. The file looks like this:
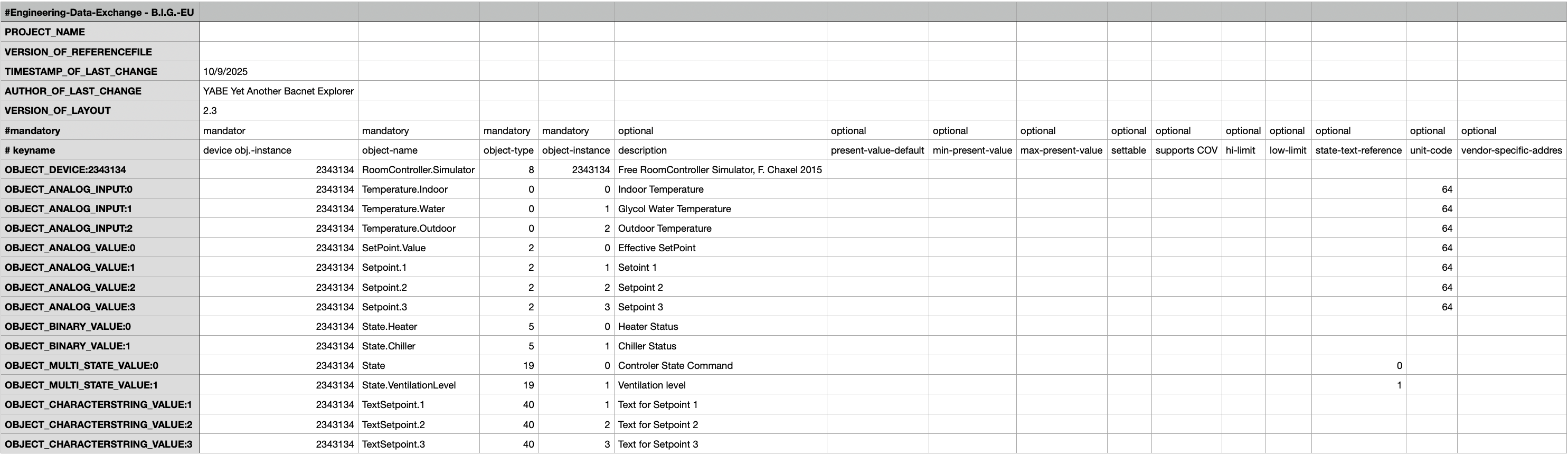
Now let’s configure the BACnet connector to use this EDE file. In the advanced configuration mode, paste the following connector configuration (make sure to use the correct path to your EDE file):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"application": {
"objectName": "TB_gateway",
"host": "YOUR_HOST",
"port": 47808,
"objectIdentifier": 599,
"vendorIdentifier": 15,
"maxApduLengthAccepted": 1476,
"segmentationSupported": "segmentedBoth",
"deviceDiscoveryTimeoutInSec": 5
},
"edeFilePath": "/path/to/your/file.ede"
}
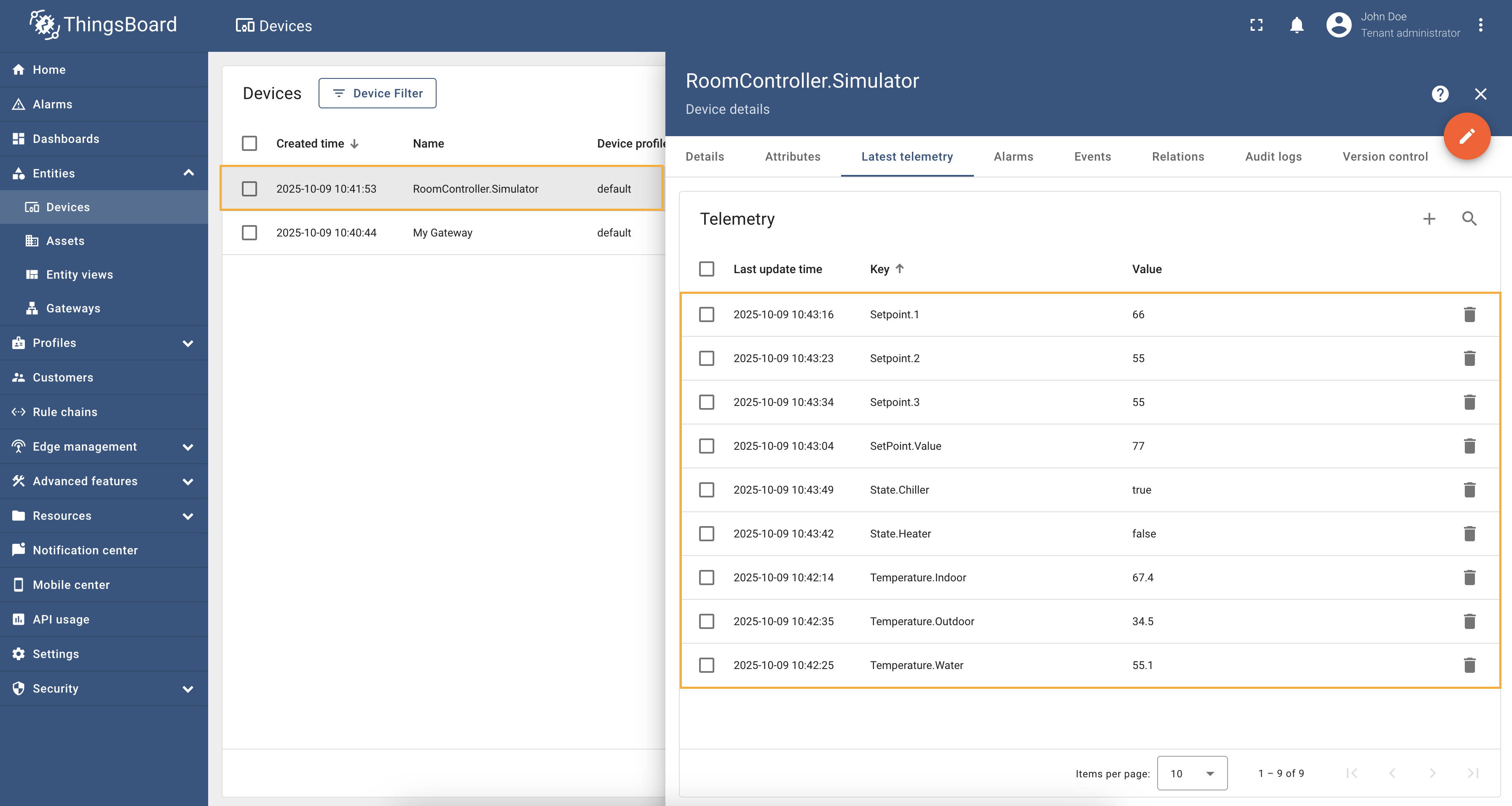
After applying the configuration, the BACnet connector will parse the EDE file and automatically configure itself to interact with the BACnet device described in the file. You can then use the connector to read data from the device, update device attributes, and send RPC commands to the device. As you can see on the screenshot below, the connector has automatically created the device with the name and profile from the EDE file, as well as all the attributes and time series from the file:
Advanced configuration
The advanced configuration section provides a detailed overview of all available parameters for the BACnet connector.
Application
The application configuration parameters are used to configure the gateway in the BACnet network.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| application.objectName | ThingsBoard Gateway | The gateway object name in the BACnet network. |
| application.host | The gateway host in the BACnet network | |
| application.port | 47808 | The gateway port in the BACnet network. |
| application.mask | The gateway mask in the BACnet network. | |
| application.networkNumber | Identifier of the network segment. | |
| application.objectIdentifier | 599 | The gateway object identifier in the BACnet network. |
| application.vendorIdentifier | 15 | The gateway vendor identifier in the BACnet network. |
| application.maxApduLengthAccepted | 1476 | Maximal length of the APDU. |
| application.segmentationSupported | segmentedBoth | The type of segmentation, can be: segmentedBoth, segmentedTransmit, segmentedReceive, noSegmentation. |
| application.deviceDiscoveryTimeoutInSec (in sec) | 5 | Timeout for discovering devices. |
| application.devicesDiscoverPeriodSeconds (in sec) | 30 | Period of time when the connector will try to discover BACnet devices. |
| application.devicesRescanObjectsPeriodSeconds (in sec) | 60 | The period of time when the connector will try to reread device objects that it failed to read last time. |
| application.loadProprietaryDevices * | false | Allow dynamically loading proprietary devices from extensions. |
Example of the application configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"application": {
"objectName": "TB_gateway",
"host": "192.168.1.168",
"port": 47808,
"objectIdentifier": 599,
"vendorIdentifier": 15,
"maxApduLengthAccepted": 1476,
"segmentationSupported": "segmentedBoth",
"networkNumber": 3,
"deviceDiscoveryTimeoutInSec": 5
}
}
Foreign device (v.3.7.6+)
The foreign device configuration parameters are used to configure the gateway as a foreign device in the BACnet network. It is useful when the gateway is behind a NAT and needs to register with a BACnet Broadcast Management Device (BBMD).
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| foreignDevice.ttl (in sec) | 900 | Time to live for the foreign device registration. |
| foreignDevice.address | 0.0.0.0 | The address of the BBMD to register with. |
Devices
The device list contains an array of BACnet devices that can be connected to the connector and interact with them. Any BACnet device not included in this array will be rejected by the connector.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| devices[].host | The host of the device. |
| devices[].port | The port of the device. |
| devices[].mask | The mask of the device. |
| devices[].networkMask | The identifier of the device network segment. |
| devices[].pollPeriod | The period of time when the connector will try to poll the BACnet device. |
| devices[].altResponsesAddresses[] | Array of alternative addresses for device responses (you can find detail examples here). |
| devices[].reportStrategy | Report strategy object using for configuring report strategy for device. |
| devices[].deviceInfo | Device info object using for configuring device name and profile. |
| devices[].deviceInfo.deviceNameExpressionSource | The source of the device name: constant, expression. |
| devices[].deviceInfo.deviceNameExpression | The device name (you can find detail examples here). |
| devices[].deviceInfo.deviceProfileExpressionSource | The source of the device profile: constant, expression. |
| devices[].deviceInfo.deviceProfileExpression | The device profile name (you can find detail examples here). |
Example of the device mapping configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
"devices": [
{
"deviceInfo": {
"deviceNameExpression": "BACnet Device ${objectName}",
"deviceProfileExpression": "default",
"deviceNameExpressionSource": "expression",
"deviceProfileExpressionSource": "constant"
},
"host": "192.168.2.110",
"port": "47808",
"pollPeriod": 10000,
"attributes": [],
"timeseries": [],
"attributeUpdates": [],
"serverSideRpc": []
}
]
}
Available variables for device name/profile expressions
You can use the following parameters for forming device name and profile:
${objectName}- the device object name of the BACnet device.${objectId}- the device object identifier of the BACnet device.${vendorId}- the device vendor identifier of the BACnet device.${address}- the device host address.${routerId}- the device router identifier.${routerName}- the device router name.${routerAddress}- the device router address.${routerVendorId}- the device router vendor identifier.
You can find detail examples here.
Device attributes and time series
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| devices[].attributes[] | This subsection contains parameters of the device data, that will be interpreted as attributes for the device. |
| devices[].attributes[].key | The name for time series on the platform. |
| devices[].attributes[].objectType | The object type in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].attributes[].objectId | The object id in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].attributes[].propertyId | The property id in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].attributes[].reportStrategy | Report strategy object using for configuring report strategy for device attribute. |
| devices[].timeseries[] | This subsection contains parameters of the device data, that will be interpreted as time series for the device. |
| devices[].timeseries[].key | The name for time series on the platform. |
| devices[].timeseries[].objectType | The object type in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].timeseries[].objectId | The object id in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].timeseries[].propertyId | The property id in the BACnet device. |
| devices[].timeseries[].reportStrategy | Report strategy object using for configuring report strategy for device time series. |
Example of the device attributes and time series configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
{
"attributes": [
{
"key": "location",
"objectType": "analogValue",
"objectId": 1,
"propertyId": "presentValue"
}
],
"timeseries": [
{
"key": "temperature",
"objectType": "analogInput",
"objectId": 2,
"propertyId": "presentValue"
}
]
}
Device attribute updates
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| devices[].attributeUpdates[] | List of attributes that will be updated on the device. | |
| devices[].attributeUpdates[].key | The name of the shared attribute on platform instance. | |
| devices[].attributeUpdates[].objectType | The object type in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].attributeUpdates[].objectId | The object id in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].attributeUpdates[].propertyId | The property id in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].attributeUpdates[].timeout (in ms) | 5000 | Timeout in milliseconds for the attribute update request. |
Example of the device attribute updates configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
{
"attributeUpdates": [
{
"key": "setpoint",
"objectType": "analogValue",
"objectId": 3,
"propertyId": "presentValue",
"timeout": 5000
}
]
}
Device RPC methods
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| devices[].serverSideRpc[] | List of RPC methods that will be sent to the device. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].method | RPC method name. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].requestType | “writeProperty” to write data and “readProperty” to read data. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].objectType | The object type in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].objectId | The object id in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].propertyId | The property id in the BACnet device. | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].priority | Priority of the value to write (optional, should be an integer from 1 to 16). | |
| devices[].serverSideRpc[].timeout (in ms) | 5000 | Timeout in milliseconds for the RPC method execution. |
Example of the device RPC methods configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
{
"serverSideRpc": [
{
"method": "set_state",
"requestType": "writeProperty",
"objectType": "analogValue",
"objectId": 3,
"propertyId": "presentValue",
"timeout": 5000
}
]
}
Additional information
Supported Object Types
The BACnet connector support the following BACnet object types:
| BACnet object id | ThingsBoard object id |
|---|---|
| Binary input | binaryInput |
| Binary Output | binaryOutput |
| Binary Value | binaryValue |
| Analog Input | analogInput |
| Analog Output | analogOutput |
| Analog Value | analogValue |
| Schedule Object | schedule |
Supported Property Identifiers
Property identifiers depend on type of the BACnet object, provided in camelCase, e.g:
- presentValue
- objectName
- objectDescription
- units
- eventState
- outOfService
- priorityArray
- relinquishDefault
- currentCommandPriority
- eventMessageTexts
- eventMessageTextsConfig
- eventAlgorithmInhibitReference
- timeDelayNormal
- weeklySchedule
- listOfObjectPropertyReferences
- location
Troubleshooting
Device discovery issues on Linux with Docker Compose
If you are running Gateway via docker compose on Linux, and you have issues with device discovery, make sure that you
have set the correct network mode in the docker compose file. So you should add the following line to tb-gateway
service in your docker compose file:
1
2
3
network_mode: "host"
extra_hosts:
- "host.docker.internal:host-gateway"
Device discovery issues on Windows with Docker Compose
BACnet connector doesn’t support device discovery on Windows OS due to the limitations of the Docker networking stack on Windows. Please use installation from source or other installation methods to run Gateway on Windows OS.
Next steps
Explore guides related to main ThingsBoard features:
- Data Visualization - how to visualize collected data.
- Device attributes - how to use device attributes.
- Telemetry data collection - how to collect telemetry data.
- Using RPC capabilities - how to send commands to/from devices.
- Rule Engine - how to use rule engine to analyze data from devices.


 and [Data mapping](/docs/iot-gateway/config/bacnet/#data-mapping) sections of this guide). Click on the “Pencil” icon on a device you want to configure attribute updates for.](https://img.thingsboard.io/gateway/bacnet-connector/examples/select-device-configuration-preview.png)