- Overview
- Create converter and integration templates
- Modify Edge Root Rule Chain for downlinks
- Assign Integration to Edge
- Send uplink message
- Send downlink message
- Next steps
Overview
HTTP integration allows existing protocols and payload formats to be converted to the ThingsBoard Edge message format and is useful in multiple deployment scenarios:
- Stream device and/or asset data from an external system, IoT platform or connectivity provider back-end.
- Stream device and/or asset data from your custom application running in the cloud.
- Connect the existing device to ThingsBoard Edge using a custom HTTP-based protocol.
Create converter and integration templates
Only the ThingsBoard Professional Edition creates converters and integration templates. So please use ThingsBoard Cloud or install your own platform instance to log in as a Tenant administrator.
Follow the steps below to add the HTTP integration:
- Go to theEdge management > Integration templates section and click the “plus” button to add a new integration. Select the “HTTP” type. Name it “Edge HTTP Integration”. Then click Next;

- The next step is to create an Uplink data converter.
Uplink is needed to convert the data coming from the device into the format needed to display it on ThingsBoard. For this example, use the following code:
One can use either TBEL (ThingsBoard expression language) or JavaScript to develop user defined functions. We recommend utilizing TBEL as it’s execution in ThingsBoard is much more efficient compared to JS.
|
Copy the following script: Choose “Create new” and paste copied code to the Decoder function section. Click “Next”;
|
|
Copy the following script: Choose “Create new” and paste copied code to the Decoder function section. Click “Next”;
|
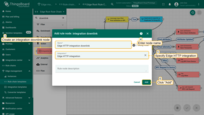
- The next step is to create a Downlink Converter.
The downlink converter converts the outbound RPC message and then the integration sends it to your device. You can customize a downlink according to your configuration. Let’s consider an example where we send an attribute update message. For this example, use the following code.
One can use either TBEL (ThingsBoard expression language) or JavaScript to develop user defined functions. We recommend utilizing TBEL as it’s execution in ThingsBoard is much more efficient compared to JS.
|
Copy the following script: Choose “Create new” and paste copied code to the Encoder function section. Click “Next”;
|
|
Copy the following script: Choose “Create new” and paste copied code to the Encoder function section. Click “Next”;
|
-
Finally, we go to the “Connection” page:
- Enter the IP address and port of your Edge instance in the format ‘host:port’ as the Base URL. Or, you can use the placeholder ${{ATTRIBUTE_KEY}} to replace the integration field with an attribute value from a specific Edge entity. In this example, we will use the placeholder ${{baseUrl}} for Base URL.
- Then click the “Add” button.

HTTP integration is created.
Modify Edge Root Rule Chain for downlinks
We can send a downlink message to the device from the Rule chain using the rule node. To send downlink over integration, we need to modify Edge Root Rule chain.
- Go to the Edge management > Rule chain templates section and click on the "Edge Root Rule Chain" to open it.
- Create an 'integration downlink' node. Specify your integration in the settings;
- Set the "Attributes Updated" and "Post attributes" links from the 'message type switch' node to the 'integration downlink' node. When the attribute is created or changes are made to the attribute, the downlink message is sent to the integration. Apply the changes.

Assign Integration to Edge
Once the converter and integration templates are created, we can assign the Integration template to Edge. Since we are using placeholder ${{baseUrl}} in the integration configuration, we need to add attribute baseUrl to Edge first. You need to provide IP address and port of your Edge instance as baseUrl attribute. Once the attribute is added, we’re ready to assign integration and verify that it’s added.
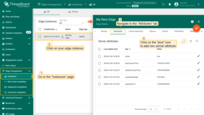
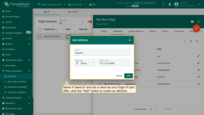
- Go to the Edge management > Instances section, click on your edge instance to open the "Edge details" window, and navigate to the "Attributes" tab. Click the "plus" button to add a new server attribute to the Edge.
- Enter the new attribute name - "baseUrl, and set the value IP:port. Then click the "Add" button.
- The "baseUrl" server attribute is now added to the edge.
- To assign the integration to the Edge, click the "Manage edge integrations" button.
- Click the "+" button at the top right of the corner. Select your integration from the drop-down menu and click the "Assign" button.
- Login to your ThingsBoard Edge instance and go to the Integrations center > Integrations section. You should see your integration. Click on it.
- In the "Integration details" window, the ${{baseUrl}} placeholder will be replaced with the value of the attribute.
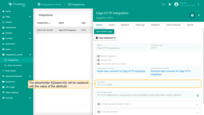
Send uplink message
To send an uplink message, you need the HTTP endpoint URL from the integration. Log in to ThingsBoard Edge and go to the Integrations center > Integrations section. Find your HTTP integration and click it. Find and copy the “HTTP endpoint URL”.
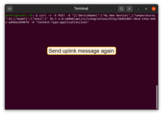
Use the command below to send a message. Remember to replace $DEVICE_NAME and $YOUR_HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL with the corresponding values.
1
curl -v -X POST -d "{\"deviceName\":\"$DEVICE_NAME\",\"temperature\":33,\"model\":\"test\"}" $YOUR_HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL -H "Content-Type:application/json"

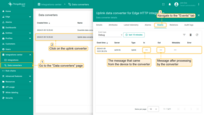
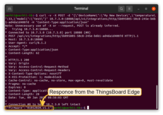
Now, select the “Events” tab in your HTTP integration. If you have done everything correctly, you will see an uplink message with the status ‘OK’. To see the message itself, click on the three dots in the “Message” column.

When you sent the message, a new device was created. The created device with data can be seen in the Entities > Devices section on the Edge:

You can also view the received data in the Uplink Converter. In the “In” and “Out” blocks of the “Events” tab:
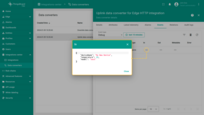
Send downlink message
Now let’s check the downlink functionality.
Let’s add a ‘firmware’ shared attribute. Go to the “Devices” section, select your device, and open the “Attributes” tab on the ThingsBoard Edge. Select the “Shared attributes” scope and click the “plus” button to create new attribute. Then set the attribute name and value (e.g., the key name is ‘firmware’, value: ‘01052020.v1.1’), and save the data.

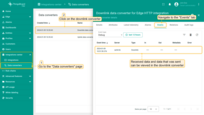
To make sure that downlink message is sent to integration, check the Events tab of the integration:

Now we need to send another message to the HTTP integration. Use the same command you used before. Remember to replace $DEVICE_NAME and $YOUR_HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL with the corresponding values.
1
curl -v -X POST -d "{\"deviceName\":\"$DEVICE_NAME\",\"temperature\":33,\"model\":\"test\"}" $YOUR_HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL -H "Content-Type:application/json"
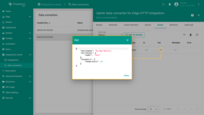
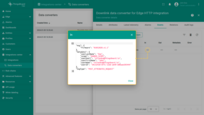
The received and sent data can be viewed in the downlink converter. The received data is displayed in “In” block of the “Events” tab.
The “Out” field shows the message sent to the device:
Next steps
-
Getting started guide - Provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard Edge features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes:
-
Installation guides - Learn how to setup ThingsBoard Edge on various available operating systems and connect to ThingsBoard Server.
-
Edge Rule Engine:
-
Rule Chain Templates - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Edge Rule Chain Templates.
-
Provision Rule Chains from cloud to edge - Learn how to provision edge rule chains from cloud to edge.
-
- Security:
- gRPC over SSL/TLS - Learn how to configure gRPC over SSL/TLS for communication between edge and cloud.
-
Features:
-
Edge Status - Learn about Edge Status page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
Cloud Events - Learn about Cloud Events page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
-
Use cases:
-
Manage alarms and RPC requests on edge devices - This guide will show how to generate local alarms on the edge and send RPC requests to devices connected to edge:
-
Data filtering and traffic reduce - This guide will show how to send to cloud from edge only filterd amount of device data:
-
- Roadmap - ThingsBoard Edge roadmap.



