- Overview
- Create Converter templates
- Create Integration template
- Modify the Edge Root Rule chain for Downlinks
- Air conditioners Dashboard
- Assign Integration to Edge
- Validation
- Next steps
Overview
OPC UA Integration allows you to stream data from the OPC UA server to ThingsBoard Edge and converts the device payloads to the ThingsBoard Edge format.
In this tutorial, we will configure the integration between ThingsBoard Edge and OPC-UA to get the air conditioners data from the OPC UA C++ Demo Server and allow the user to switch on/off any air conditioner using the Integration downlink feature.
Prerequisites
- Download and install the OPC UA C++ Demo Server.
Note: This server currently supports Windows only.
- Launch the UA Admin Dialog after installation.
- Make sure the hostname/IP address and port are configured correctly.
You'll need these details to set up the OPC-UA integration in ThingsBoard.

- Launch the UaCPPServer.
A console window will appear displaying the server's endpoint URLs

Create Converter templates
Converter and Integration templates are created on the Cloud, so please log in as Tenant administrator to cloud instance.
Uplink Converter template
Before creating the Integration template, create an Uplink and Downlink converter templates on the Converters templates page.
- Uplink Converter is a script that parses and transforms the data received by the OPC UA integration.
- Downlink Converter parses and transforms the data sent from ThingsBoard Edge to the format that is consumed by the existing device(s).
First, we need to create the Uplink Data converter that will be used to receive the messages from the OPC UA server. The converter should transform the incoming payload into the required message format. The resulting message must contain the deviceName and deviceType. These fields are used to submit the data to the correct device. If a device is not found, a new device is created. Here is a sample of the payload from the OPC UA Server:
Payload:
1
2
3
{
"temperature": "72.15819999999641"
}
Metadata:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
"opcUaNode_namespaceIndex": "3",
"opcUaNode_name": "AirConditioner_1",
"integrationName": "OPC-UA Airconditioners",
"opcUaNode_identifier": "AirConditioner_1",
"opcUaNode_fqn": "Objects.BuildingAutomation.AirConditioner_1"
}
We will take the opcUaNode_name metadata value and map it to the deviceName and set the deviceType as default.
However, you can use a different mapping in your specific use cases.
We will also retrieve the values of the temperature, humidity and powerConsumption fields and use them as device telemetries.
Click the “plus” button and select the “Create new converter” option. To view the events, enable “Debug” mode. In the “Function decoder” field, enter a script to parse and transform data.
Example for the Uplink converter:
The purpose of the decoder function is to parse the incoming data and metadata into a format that ThingsBoard Edge can consume.
- deviceName and deviceType are required, while attributes and telemetry are optional.
- Attributes and telemetry are flat key-value objects. Nested objects are not supported.
The decoder function can be changed during converter creation or later.
- If the converter has already been created, click it to open the “Data converter details” window.
- To edit the converter, click the “Edit” button (the “pencil” icon).
- Copy the configuration example for the converter (or your own configuration) and paste it into the decoder function.
- To save the changes, click the “Save” button (the “checkmark” icon).
Downlink Converter template
To send Downlink messages from the ThingsBoard Edge to the OPC UA node, we need to define a Downlink converter.
In general, the output of the Downlink converter should have the following structure:
1
2
3
4
5
[{
"contentType": "JSON",
"data": "{\"writeValues\":[],\"callMethods\":[{\"objectId\":\"ns=3;s=AirConditioner_1\",\"methodId\":\"ns=3;s=AirConditioner_1.Stop\",\"args\":[]}]}",
"metadata": {}
}]
- contentType: Defines how the data is encoded {TEXT | JSON | BINARY}. OPC UA Integration uses JSON encoding by default.
- data: The actual data that will be processed by OPC UA Integration and sent to the target OPC UA nodes:
- writeValues: The array of write values methods OPC UA Write Value format:
- nodeId: The target node (
ns=<namespaceIndex>;<identifiertype>=<identifier>) - value: The value to write
- nodeId: The target node (
- callMethods: The array of call methods OPC UA Call Methods format:
- objectId: The target object
- methodId: The target method
- args: The array of method input values
- writeValues: The array of write values methods OPC UA Write Value format:
- metadata: Is not used for the OPC UA Integration and can be empty.
You can customize a downlink according to your configuration:
- The converter processes the RPC command to the device using the setState method and a boolean params value to call the ‘Start’ or ‘Stop’ method of the air conditioner.
- The destination node is determined using the deviceName field of the incoming message metadata.
Create the Downlink in Converter templates page as well. To see the events, check the Debug checkbox.
An example of the downlink converter:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/** Encoder **/
var data = {
writeValues: [],
callMethods: []
};
if (msgType === 'RPC_CALL_FROM_SERVER_TO_DEVICE') {
if (msg.method === 'setState') {
var targetMethod = msg.params === 'true' ? 'Start' : 'Stop';
var writeValue = {
nodeId: 'ns=' + metadata['cs_namespaceIndex'] +';s=' + metadata['deviceName'],
value: msg.params
};
data.writeValues.push(writeValue);
var callMethod = {
objectId: 'ns=' + metadata['cs_namespaceIndex'] +';s=' + metadata['deviceName'],
methodId: 'ns=' + metadata['cs_namespaceIndex'] +';s=' + metadata['deviceName']+'.'+targetMethod,
args: []
};
data.callMethods.push(callMethod);
}
}
var result = {
contentType: "JSON",
data: JSON.stringify(data),
metadata: {}
};
return result;
Create Integration template
Now that the Uplink and Downlink converter templates have been created, it is possible to create an integration:
- Go to the Integration templates section and click Add new integration button.
- Name it OPC-UA air conditioners, select the OPC-UA type, enable Debug mode, and add recently created Uplink and Downlink converters from the corresponding drop-down menus.
The other integration field values:
- Application name: <empty> (client application name)
- Application uri: <empty> (client application uri)
- Host: ${{endpointHost}} (we will add Edge attribute endpointHost in next steps)
- Port: Endpoint Port (see Prerequisites)
- Scan period in seconds: 10 (how often to rescan OPC UA nodes)
- Timeout in milliseconds: 5000 (the timeout, in milliseconds, before failing a request to OPC UA server)
- Security: None (can be Basic128Rsa15 / Basic256 / Basic256Sha256 / None)
- Identity: Anonymous (can be Anonymous / Username)
- Mapping:
- MappingType: Fully Qualified Name (can be Fully Qualified Name / ID)
- Device Node Pattern:
Objects\.BuildingAutomation\.AirConditioner_\d+$(regular expression used to match scanned OPC UA Node FQNs/IDs to device name. In this sample, path on OPC UA Explorer isObjects/BuildingAutomation/AirConditioner_X, where X is a number from 1 to N. That’s why we useObjects\.BuildingAutomation\.AirConditioner_\d+$as regular expression, because\d+means any number from 1 to N, and$means the end of the string) - The Subscription tags (the list of node tags (Path) to subscribe with mappings to keys (Key) used in the output message):
- state - State
- temperature - Temperature
- humidity - Humidity
- powerConsumption - PowerConsumption
To save the Integration, click the Add button.
Modify the Edge Root Rule chain for Downlinks
We can send a downlink message to the device from Rule chain using the rule node:
- To send a downlink over integration, we need to modify the Edge Root Rule chain.
- Add two rule nodes: the originator fields and integration downlink nodes.
- Set the RPC Request to Device link to the originator fields node and configure to add the originator name and type to the message metadata — in the downlink converter name of the device will be used to set proper OPC-UA node.
- And then add the Success link from the originator fields node to integration downlink node.
- When the RPC request is going to be triggered to a device on the Edge, the downlink message will be sent to the integration.
Air conditioners Dashboard
To visualize the air conditioners data and test the RPC commands, create the air conditioners dashboard and assign it to the Edge. First, please download the airconditioners_dashboard.json file.
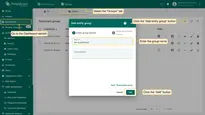
- Go to the Dashboard section and select the "Groups" tab. Click the "Add entity group" button to create a new Air conditioner group.
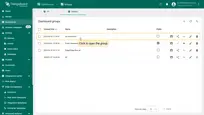
- Open the newly created Air conditioner group.
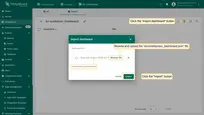
- Click the "Import dashboard" button and browse for recently downloaded "airconditioners_dashboard.json" file. To proceed, click the "Import" button.
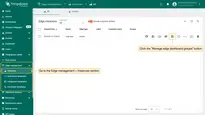
- In the Edge instance, go to the Edge management > Instances section and click the Manage edge dashboard groups button.
- Click the "Assign to edge" button and select the Air conditioner group from the drop-down menu to assign it to the Edge.
Assign Integration to Edge
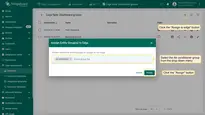
Once the converters and integration templates are created, we can assign the Integration template to the Edge. Since we are using placeholder ${{endpointHost}} in the integration configuration, we need to add the endpointHost attribute to the Edge first. You need to provide the Endpoint Host of the OPC-UA Server (see Prerequisites). Once the attribute is added, we are ready to assign the integration and verify that it has been added.
- Add the endpointHost attribute to the Edge and set the 192.168.2.153 value as your Edge.
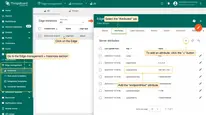
- Click the Manage Integrations button of Edge entity.
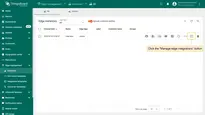
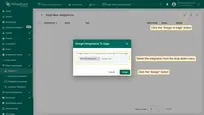
- Assign the Integration to the Edge.
- Login to your ThingsBoard Edge instance and open the Integrations page. The placeholder is going to be replaced by the attribute value
Validation
Let’s verify that the integration has been successfully started on the Edge and that the connection to the OPC-UA Demo Server has been established.
- Go to the Device groups page. You will see the Air conditioners group.
- You can see up-to-the-minute telemetry from all 10 air conditioners.
- Open the details of one of the Air conditioners and select the Latest Telemetry tab.
- You will see that telemetry values are updated frequently.
- Go to the Dashboards section and open the Air conditioners dashboard.
- You can see up-to-the-minute telemetry from all 10 air conditioners.
- Open the “Air conditioner details” page by clicking the “Details” button in the Entities widget.
- You will find the Air conditioner status light green.
- To turn off the air conditioner, click the On/Off Round switch.
- The air conditioner status light will turn gray, the temperature and humidity begin to rise, and the power consumption stops.
Next steps
-
Getting started guide - Provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard Edge features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes:
-
Installation guides - Learn how to setup ThingsBoard Edge on various available operating systems and connect to ThingsBoard Server.
-
Edge Rule Engine:
-
Rule Chain Templates - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Edge Rule Chain Templates.
-
Provision Rule Chains from cloud to edge - Learn how to provision edge rule chains from cloud to edge.
-
- Security:
- gRPC over SSL/TLS - Learn how to configure gRPC over SSL/TLS for communication between edge and cloud.
-
Features:
-
Edge Status - Learn about Edge Status page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
Cloud Events - Learn about Cloud Events page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
-
Use cases:
-
Manage alarms and RPC requests on edge devices - This guide will show how to generate local alarms on the edge and send RPC requests to devices connected to edge:
-
Data filtering and traffic reduce - This guide will show how to send to cloud from edge only filterd amount of device data:
-
- Roadmap - ThingsBoard Edge roadmap.





















