- Data Flow Overview
- Prerequisites
- Create ThingsBoard Integration
- Create TBMQ HTTP Integration
- Sending an Uplink Message
TBMQ HTTP Integration provides a simple and efficient way to forward MQTT messages from devices to an external system using the HTTP protocol. It acts as a bridge between TBMQ and external applications, ensuring seamless and reliable data exchange.
Data Flow Overview
TBMQ HTTP Integration enables forwarding MQTT messages to an external HTTP service:
- Device (client) publishes an MQTT message to a topic that matches the Integration’s Topic Filters.
- TBMQ broker receives the message and forwards to TBMQ Integration Executor.
- TBMQ Integration Executor processes the message, formats it as an HTTP request, and forwards it to the external service.
- External service receives the request and processes the data accordingly.

Prerequisites
Before setting up the integration, ensure the following:
- A running TBMQ instance.
- An external service ready to receive HTTP requests (e.g., ThingsBoard Cloud).
- A client capable of publishing MQTT messages (e.g., TBMQ WebSocket Client).
Create ThingsBoard Integration
In this tutorial, we use ThingsBoard as the external service receiving HTTP requests from TBMQ. However, any other HTTP-compatible service can be used.
Follow the official ThingsBoard HTTP Integration Guide to create an integration on ThingsBoard Cloud.
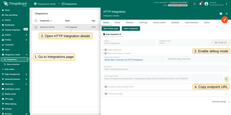
Once the HTTP Integration is created:
- Open the details page and enable debug mode to verify data reception.
- Copy the HTTP endpoint URL, as this will be needed in the next step.
Create TBMQ HTTP Integration
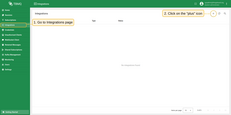
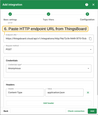
- Go to the Integrations page and click the “+” button to create a new integration.
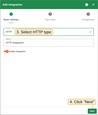
- Select HTTP as the integration type and click Next.
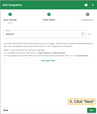
- On the Topic Filters page click Next to subscribe to the default topic
tbmq/#. - In the Configuration step, paste the Endpoint URL from the ThingsBoard Integration.
- Open Advanced settings and set Payload content type to
JSON. - Click Add to save the integration.
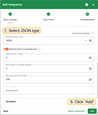
You can test the connectivity to the configured HTTP endpoint by sending a HEAD request using the ‘Check connection’ button.
Topic Filters
Topic filters define MQTT-based subscriptions and act as triggers for TBMQ HTTP Integration. When the broker receives a message matching configured topic filters, the integration processes it and forwards the data to the specified external system.
If the integration is configured with the topic filter:
1
tbmq/devices/+/status
Then, any message matching this pattern will trigger the integration, including:
1
2
tbmq/devices/device-01/status
tbmq/devices/gateway-01/status
Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Send only message payload | If enabled, the incoming message’s payload is forwarded as is. If disabled, a JSON object with the payload and other properties is sent. |
| Endpoint URL | The external service URL where HTTP requests are sent. |
| Request Method | Defines how the request is made. Supported methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE. |
| Credentials | Supported authentication options: |
| Anonymous – No authentication. | |
Basic Authentication – Uses Username and Password for authentication. |
|
| PEM-based authentication – Uses PEM certificate to authenticate. | |
| Headers | A collection of key-value pairs added to the HTTP request headers. |
| Payload Content Type | Defines the format of the request body. Supported: JSON, Text, Binary (Base64). |
| Send as binary on parsing error | If enabled, messages with a failed JSON or Text parsing attempt will be sent as a binary payload. If disabled, failed messages will not be sent. |
| Read Timeout | Maximum time the request waits for a response before timing out. |
| Max Parallel Requests | Limits the number of concurrent HTTP requests. |
| Max Response Size | Defines the maximum allowed size for incoming responses. |
| Metadata | Custom metadata that can be used for additional processing. |
Events
TBMQ provides logging for integration-related events, allowing users to debug and troubleshoot integration behavior. Below are three ‘Event’ types:
-
Lifecycle Events – Logs events such as
Started,Created,Updated,Stopped, etc. -
Statistics – Provides insights into integration performance, including the number of processed messages and occured errors.
-
Errors – Captures failures related to authentication, timeouts, payload formatting, or connectivity issues with the external service.
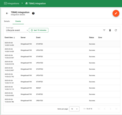
Lifecycle Events – Logs events such as Started, Created, Updated, Stopped, etc.
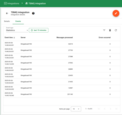
Statistics – Provides insights into integration performance, including the number of processed messages and occured errors.
Errors – Captures failures related to authentication, timeouts, payload formatting, or connectivity issues with the external service.
Sending an Uplink Message
To send a message, follow these steps:
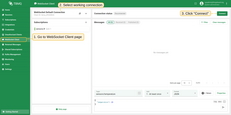
- Navigate to the WebSocket Client page.
- Select ‘WebSocket Default Connection’ or any other available working connection, then click Connect. Make sure the ‘Connection status’ is shown as
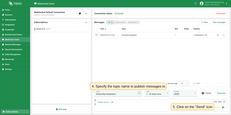
Connected. - Set the ‘Topic’ field to
tbmq/http-integrationto match the Integration’s ‘Topic Filter’tbmq/#. - Click the Send icon to publish the message.
- If successfull, the message should appear in the ‘Messages’ table.
Once the message is published:
- In the ThingsBoard Cloud open the HTTP Integration details.
- Go to the Events tab.
- If the setup is correct, you should see an event with the status ‘OK’ and a message payload similar to:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
{
"payload": {
"temperature": 25
},
"topicName": "tbmq/http-integration",
"clientId": "tbmq_7QUvZzow",
"eventType": "PUBLISH_MSG",
"qos": 1,
"retain": false,
"tbmqIeNode": "tbmq_ie_node",
"tbmqNode": "tbmq_node",
"ts": 1742553324248,
"props": {},
"metadata": {
"integrationName": "HTTP integration"
}
}
Message description:
- payload: Content of the MQTT message.
- topicName: The MQTT topic to which the message was published.
- clientId: The ID of the MQTT client that published the message.
- eventType: Type of MQTT event, here it’s a published message (the only supported type for now).
- qos: Quality of Service level used for the incoming message.
- retain: Indicates if the message is a retained MQTT message.
- tbmqIeNode: Node ID of the Integration Executor service that handled the message.
- tbmqNode: Node ID of the TBMQ broker that received the message.
- ts: Timestamp (in milliseconds) when the message was received.
- props: MQTT 5.0 user properties or other MQTT properties.
- metadata: Additional metadata added from integration configuration, e.g., the name of the integration that handled the message, added by default.

