TBMQ Kafka Integration enables seamless communication with Apache Kafka. It allows TBMQ to publish messages to the external Kafka clusters and can be useful for the following scenarios:
- Streaming IoT Data – Forwarding device telemetry, logs, or events to Kafka for processing and storage.
- Event-Driven Architectures – Publishing messages to Kafka topics for real-time analytics and monitoring.
- Decoupled System Communication – Using Kafka as a buffer between TBMQ and downstream applications.
Data Flow Overview
TBMQ Kafka Integration processes messages and forwards them to an external Kafka cluster in the following steps:
- Device (client) publishes an MQTT message to a topic that matches the Integration’s Topic Filters.
- TBMQ broker receives the message and forwards to TBMQ Integration Executor.
- TBMQ Integration Executor processes the message, formats it accordingly, and sends it to a configured Kafka topic.
- Kafka consumers process the message in downstream systems.

Prerequisites
Before setting up the integration, ensure the following:
- A running TBMQ instance.
- An external service ready to receive Kafka message (e.g. Confluent Cloud).
- A client capable of publishing MQTT messages (e.g., TBMQ WebSocket Client).
Create TBMQ Kafka Integration
- Navigate to the Integrations page and click the ”+” button to create a new integration.
- Select Kafka as the integration type and click Next.
- On the Topic Filters page click Next to subscribe to the default topic
tbmq/#.
- In the Configuration step enter the Bootstrap servers (Kafka broker addresses).
|
Configure kafka integration In Confluent select the created environment, then open Cluster, Cluster settings. After, find Bootstrap server URL, it looks like URL_OF_YOUR_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER:9092. Then copy it to integration: Also, will be needed to add several Other properties, namely:
To generate the required API key and secret for it, in the cluster you must go to the Data Integration menu, select the API Keys submenu, pick Create key and Select the Scope for the API Key. Here you will see the key and secret to it, which should be used in the integration properties. It remains to create a topic on Confluent. To do this, select the “Topics” menu, select “Create Topics”, set the name to tbmq.messages. |
- Click Add to save the integration.
You can test the connectivity to the configured Kafka brokers by using the ‘Check connection’ button. This action creates an admin client that connects to the Kafka cluster and verifies whether the specified topic exists on the target brokers. Even if the topic is missing, you can still proceed with creating the integration. If the Kafka cluster has
auto.create.topics.enableset totrue, the topic will be automatically created when the first message is published.
Topic Filters
Topic filters define MQTT-based subscriptions and act as triggers for TBMQ HTTP Integration. When the broker receives a message matching configured topic filters, the integration processes it and forwards the data to the specified external system.
If the integration is configured with the topic filter:
1
tbmq/devices/+/status
Then, any message matching this pattern will trigger the integration, including:
1
2
tbmq/devices/device-01/status
tbmq/devices/gateway-01/status
Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Send only message payload | If enabled, only the raw message payload is forwarded. If disabled, TBMQ wraps the payload in a JSON object containing additional metadata. |
| Bootstrap servers | The Kafka broker addresses (comma-separated list of hostnames/IPs and ports). |
| Topic | The Kafka topic where messages will be published. |
| Key | (Optional) Used for partitioning messages. If specified, Kafka hashes the key to consistently assign messages to the same partition. |
| Client ID prefix | (Optional) Defines the prefix for the Kafka client ID. If not set, the default tbmq-ie-kafka-producer is used. |
| Automatically retry times if fails | Number of retries before marking a message as failed. |
| Produces batch size in bytes | Maximum batch size before sending messages to Kafka. |
| Time to buffer locally (ms) | Time in milliseconds to buffer messages locally before sending. |
| Client buffer max size in bytes | Maximum memory allocated for buffering messages before sending them to Kafka. |
| Number of acknowledgments | Specifies Kafka’s acknowledgment mode: all, 1, 0. |
| Compression | Defines the compression algorithm used for messages: none, gzip, snappy, lz4, zstd. |
| Other properties | A collection of key-value pairs for additional Kafka producer configurations. |
| Kafka headers | Custom headers added to Kafka messages. |
| Metadata | Custom metadata that can be used for processing and tracking. |
Events
TBMQ provides logging for integration-related events, allowing users to debug and troubleshoot integration behavior. Below are three ‘Event’ types:
-
Lifecycle Events – Logs events such as
Started,Created,Updated,Stopped, etc. -
Statistics – Provides insights into integration performance, including the number of processed messages and occured errors.
-
Errors – Captures failures related to authentication, timeouts, payload formatting, or connectivity issues with the external service.
Lifecycle Events – Logs events such as Started, Created, Updated, Stopped, etc.
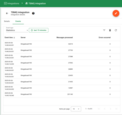
Statistics – Provides insights into integration performance, including the number of processed messages and occured errors.
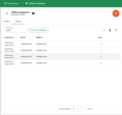
Errors – Captures failures related to authentication, timeouts, payload formatting, or connectivity issues with the external service.
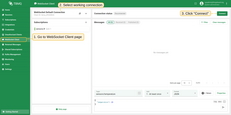
Sending an Uplink Message
To send a message, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the WebSocket Client page.
- Select ‘WebSocket Default Connection’ or any other available working connection, then click Connect. Make sure the ‘Connection status’ is shown as
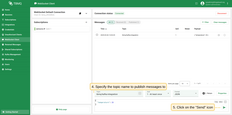
Connected. - Set the ‘Topic’ field to
tbmq/kafka-integrationto match the Integration’s ‘Topic Filter’tbmq/#. - Click the Send icon to publish the message.
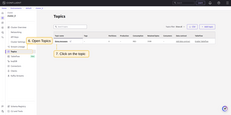
- If successful, the message should be available in your Kafka service under the topic
tbmq.messages.