- Basic authentication overview
- Configure provider
- Credentials matching
- Credentials ID
- Authorization
- MQTT Example based on Client ID, Username and Password
- MQTTS Example based on Client ID, Username and Password
- Next steps
Basic authentication remains one of the most common methods for authenticating MQTT clients due to its simplicity and native support in the MQTT protocol. It is often used in scenarios where clients are provisioned with predefined credentials — such as IoT devices connecting to private networks, internal system integrations, or deployments with straightforward access control requirements. When combined with secure transport (TLS), it provides a reliable and widely adopted authentication option for many MQTT use cases.
Basic authentication overview
Basic authentication allows MQTT clients to authenticate using credentials sent in the CONNECT packet — such as clientId, username, and password.
TBMQ uses these credentials to generate a unique credentialsId and match against the stored MQTT client credential records using flexible matching strategies.
To optimize authentication performance, TBMQ maintains credentials in Redis for fast lookups, while PostgreSQL ensures reliable persistence.
The following sections explain provider configuration, credential matching, credentialsId generation, and how authorization is applied after successful authentication.
Configure provider
You can check the authentication provider status, enable or disable it directly from the TBMQ user interface, making it easy to manage authentication behavior without modifying configuration files or restarting the broker.
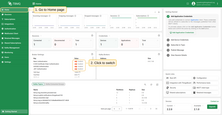
- On the Home page, in the Broker Settings card, you’ll find quick-toggle buttons for each available authentication provider. Click the button next to the desired provider to enable or disable it.
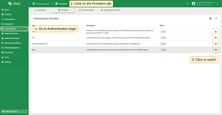
- On the Authentication Providers page, you have more control and visibility:
- You can enable or disable a provider directly from the table by clicking the Switch button in the corresponding row.
- For more detailed management, click on a provider to open its details page, where you can change the status or other parameters.
Credentials matching
The following are the possible combinations of Basic credentials matchers:
- clientId - checks if the connecting client has specified clientId.
- username - checks if the connecting client has specified a username.
- clientId and username - checks if the connecting client has specified both clientId and username.
- username and password - checks if the connecting client has specified both username and password.
- clientId and password - checks if the connecting client has specified both clientId and password.
- clientId, username and password - checks if the connecting client has specified clientId, username, and password.
Credentials ID
When a client connects, the combination of the username, password, and clientId from the CONNECT packet is matched with the persisted credentials to authenticate the client.
The matching is based on the auto-generated credentialsId field from the MQTT client credentials.
The credentialsId is generated as follows:
- credentialsId =
username|$CLIENT_USERNAMEwhen only username is present; - credentialsId =
client_id|$CLIENT_IDwhen only client ID is present; - credentialsId =
mixed|$CLIENT_USERNAME|$CLIENT_IDwhen both username and client ID are present.
Where $CLIENT_USERNAME refers to the specified username, $CLIENT_ID refers to the specified client ID from the CONNECT packet.


Authorization
After the user has been authenticated, it is possible to restrict the client’s access to topics they can publish or subscribe to.
To provide flexible control over authorization rules, TBMQ uses regular expressions.
For example, to allow clients to publish or subscribe to all topics that begin with city/, an authorization rule should be created with the value city/.*.
For the Basic type, authorization is configured through the pubAuthRulePatterns and subAuthRulePatterns of the corresponding MQTT client credentials. Therefore, for each Basic MQTT client credential, you can configure the authorization rules for the topics that these clients can access.
The pubAuthRulePatterns and subAuthRulePatterns are based on regular expression syntax. For example,
1
2
3
4
{
"pubAuthRulePatterns": ["country/.*"],
"subAuthRulePatterns": ["city/.*"]
}
The following configuration allows clients to publish messages to topics that start with country/ and subscribe to topics that start with city/.

MQTT Example based on Client ID, Username and Password
For this option, you should populate Client ID, Username and Password in the MQTT client credential. MQTT clients will be able to connect if they specify correct combination of client ID, username and password.
Let’s review a simple command to publish message using MQTT client ID, username and password to the TBMQ. The command is using plain MQTT without TLS:
1
mosquitto_pub -d -q 1 -h "YOUR_TBMQ_HOST" -p "1883" -t "sensors/temperature" -i "YOUR_CLIENT_ID" -u "YOUR_CLIENT_USERNAME" -P "YOUR_CLIENT_PASSWORD" -m {"temperature":25}
where:
- YOUR_TBMQ_HOST is the host of your TBMQ instance;
- YOUR_CLIENT_ID is your client id;
- YOUR_CLIENT_USERNAME, YOUR_CLIENT_PASSWORD is your client username and password.
MQTTS Example based on Client ID, Username and Password
One-way SSL authentication is a standard authentication mode, where your client device verifies the identity of a server using server certificate. Follow the MQTT over SSL guide to provision server certificate for your own TBMQ instance.
Let’s review a simple command to publish message using MQTT client ID, username and password to the TBMQ. The command is using MQTTS:
1
mosquitto_pub -d -q 1 --cafile YOUR_PEM_FILE -h "YOUR_TBMQ_HOST" -p 8883 -t "sensors/temperature" -i "YOUR_CLIENT_ID" -u "YOUR_CLIENT_USERNAME" -P "YOUR_CLIENT_PASSWORD" -m {"temperature":25}
where:
- YOUR_PEM_FILE is your CA file;
- YOUR_TBMQ_HOST is the host of your TBMQ instance;
- YOUR_CLIENT_ID is your client id;
- YOUR_CLIENT_USERNAME, YOUR_CLIENT_PASSWORD is your client username and password.
Next steps
-
Getting started guide - This guide provide quick overview of TBMQ.
-
Installation guides - Learn how to set up TBMQ using Docker or deploy it in K8S environments on AWS, GCP, and Azure.
-
Configuration guide - Learn about TBMQ configuration files and parameters.
-
MQTT client type guide - Learn about TBMQ client types.
-
Integration with ThingsBoard - Learn about how to integrate TBMQ with ThingsBoard.