TBMQ provides set of security features designed to protect MQTT communication, control client access, and enforce topic-level permissions. These features cover key aspects of MQTT security — from connection level settings to fine-grained authorization rules — and offer flexible configuration options for a variety of deployment scenarios.
The overview page introduces the three core areas of MQTT security in TBMQ: connection level security, authentication, and authorization. Each section below explains the role of these components, how they can be configured, and how they interact within the broker’s security model.
Connection level security
Connection-level security focuses on configuring how clients connect to the broker. It defines supported transport protocols, encryption options, and network-level parameters — all essential to establishing a secure communication channel before authentication and authorization are applied. In TBMQ, this is achieved through the configuration of MQTT listeners, which support both encrypted and unencrypted protocols (TCP, TLS, WebSockets). Each listener exposes configurable properties — such as ports, host addresses, and performance tuning options — that can be set via configuration files or overridden using environment variables. For TLS and WebSocket Secure (WSS) listeners, encryption parameters such as certificates and supported protocols can also be configured.
Authentication
Authentication verifies the identity of clients attempting to connect. It is the process of validating client credentials before granting access to the broker. Supported authentication methods include: Basic (username/password), X.509 Certificate Chain, JWT, and SCRAM.
Providers management
| Available since TBMQ Version 2.2 |
Authentication methods are implemented as pluggable authentication providers:
- Basic — Authenticates clients using a clientId, username, and password sent in the
CONNECTpacket. - X.509 Certificate Chain — Uses the client’s X.509 certificate chain during TLS handshake for authentication.
- JWT (JSON Web Token) — Authenticates clients using a signed JWT passed in the password field of the
CONNECTpacket. - SCRAM — Performs a secure challenge-response using hashed credentials to authenticate without sending the actual password (MQTT 5.0 only).
Each provider can be individually enabled, disabled, and configured to meet requirements for different deployment use cases.
You can check the authentication provider status, enable or disable it directly from the TBMQ user interface, making it easy to manage authentication behavior without modifying configuration files or restarting the broker.
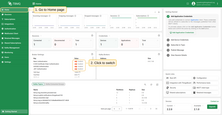
- On the Home page, in the Broker Settings card, you’ll find quick-toggle buttons for each available authentication provider. Click the button next to the desired provider to enable or disable it.
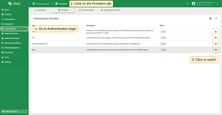
- On the Authentication Providers page, you have more control and visibility:
- You can enable or disable a provider directly from the table by clicking the Switch button in the corresponding row.
- For more detailed management, click on a provider to open its details page, where you can change the status or other parameters.
Providers execution order
| Available since TBMQ Version 2.2 |
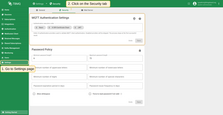
TBMQ processes authentication providers in a configurable execution order. This can be configured from the MQTT Authentication Settings page designed to configure key MQTT authentication-related parameters.
At the current stage, we have only one parameter in this section called Authentication Execution Order. It defines the order in which the broker will use authentication providers to validate MQTT client authentication.
Key rules:
- Disabled providers will be skipped in the authentication flow.
- The authentication flow stops at the first successful result or after evaluation of all enabled providers.
- If all providers are disabled, the client will be authenticated without MQTT client credentials validation.
Authorization
Authorization involves granting or denying access to specific resources or actions based on the authenticated client’s privileges. To achieve this, define topic-level access control by applying configurable rules that determine whether a client can publish to or subscribe from specific topics. TBMQ uses regular expression–based topic patterns to enforce these rules. Authorization settings are typically configured per client credentials. Only JWT-based authentication supports defining authorization rules at the provider level, allowing dynamic, token-driven access control.
Next steps
-
Getting started guide - This guide provide quick overview of TBMQ.
-
Installation guides - Learn how to set up TBMQ using Docker or deploy it in K8S environments on AWS, GCP, and Azure.
-
Configuration guide - Learn about TBMQ configuration files and parameters.
-
MQTT client type guide - Learn about TBMQ client types.
-
Integration with ThingsBoard - Learn about how to integrate TBMQ with ThingsBoard.