- Register an account on Loriot
- Create Loriot integration
- Send Uplink message
- Advanced Usage: Create Downlink Converter
- Next steps
Loriot is LoRaWAN network designed for connecting your devices using LoRaWAN stack. After integrating LORIOT with the ThingsBoard, you can connect, communicate, process and visualize data from devices in the ThingsBoard IoT platform.
Register an account on Loriot
Here's how to get started with Loriot:
- Visit the Loriot website.
- Choose a service package — for example, select the Community Public Network Server.
- Pick your preferred region and country.
- Complete the registration process and log in to your Loriot account.

* The Loriot interface may change in the future.
Create Loriot integration
You will need to have access to ThingsBoard Professional Edition. The easiest way is to use ThingsBoard Cloud server. The alternative option is to install ThingsBoard using installation guide.
Let’s move on to setting up the integration between the ThingsBoard platform and Loriot.
1. Basic settings.
- Sign in to your ThingsBoard account.
- Navigate to the “Integrations” page under the “Integrations center” section. Click “plus” button to add a new integration.
- From the list, select the integration type “Loriot”.
- If you’d like to monitor events and troubleshoot, enable debug mode.
Debug mode
Enabling debug mode allows you to track events, states, and potential errors related to the execution of integrations. This greatly simplifies development and troubleshooting.
Debug mode settings can be combined or disabled entirely.
- Click “Next”.

2. Uplink data converter.
Uplink is necessary in order to convert the incoming data from the device into the required format for displaying them in ThingsBoard.
Starting from ThingsBoard 4.0, we have simplified the process of writing converters for Loriot integration. You can now easily choose where the message fields from the integration should go (attributes or telemetry) without manually defining this in the decoder function.
Note: Converters created before the release of ThingsBoard 4.0 will still be available and will continue to function properly.
Let’s review sample uplink message from Loriot:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"cmd" : "rx",
"EUI" : "BE7A000000000552",
"ts" : 1470850675433,
"ack" : false,
"fcnt" : 1,
"port" : 1,
"data" : "2A3F",
"freq" : 868500000,
"dr" : "SF12 BW125 4/5",
"rssi" : -130,
"snr" : 1.2
}
As you can see the unique device id arrives in the “EUI” field. We will use it as a device name in ThingsBoard.
Device data is encoded in the “data” field. The encoded data here is:
1
"data": "2A3F"
Let’s convert them into temperature and humidity values.
2A is the value for temperature. In decoded form it will be 42
3F is the value for humidity. In decoded form it will be 63
Let’s return to configuring the integration:
- Enter a name for the converter. It must be unique.
- To view the events, enable debug mode.
- In the “Main decoding configuration” section
- Select the entity type (Device or Asset) that will be created as a result of the integration, and specify the entity name. The $eui pattern will dynamically fetch the device's unique identifier from the Loriot message.
Example: If the entity name is set as Device $eui, and the incoming message contains: “EUI”: “BE7A000000000552”, the converter will replace $eui with “BE7A000000000552”. The final device name will be: “Device BE7A000000000552”.
- Use the existing script for parsing and transforming data, or provide your own custom script.
- Select the entity type (Device or Asset) that will be created as a result of the integration, and specify the entity name. The $eui pattern will dynamically fetch the device's unique identifier from the Loriot message.

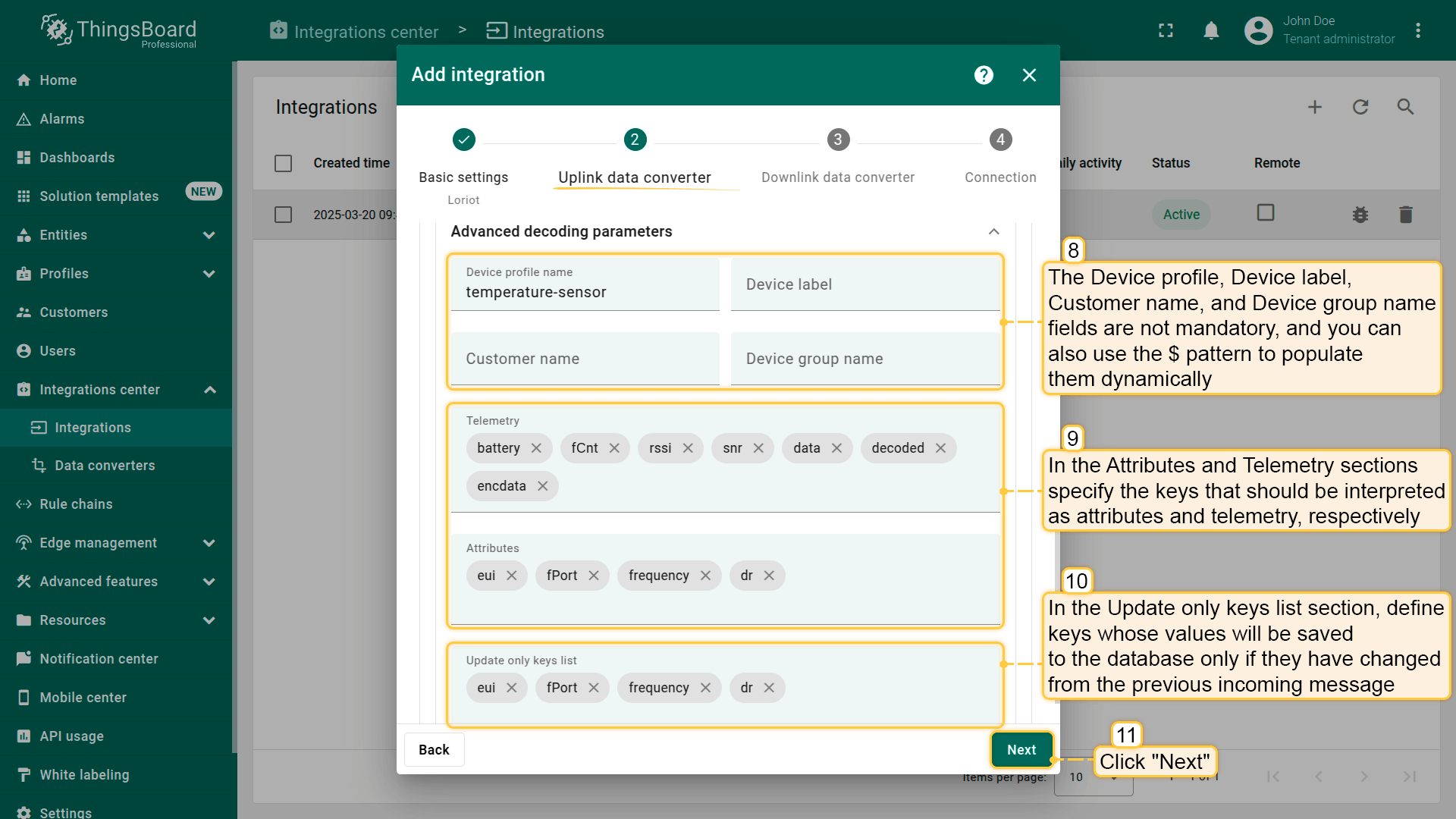
- Advanced decoding parameters” section:
- The Device profile, Device label, Customer name, and Device group name fields are not mandatory, and you can also use the $ pattern to populate them dynamically.
- In the Attributes and Telemetry sections specify the keys that should be interpreted as attributes and telemetry, respectively.
- In the Update only keys list section, define keys whose values will be saved to the database only if they have changed from the previous incoming message.This applies to both Attributes and Telemetry, helping optimize data storage.
- Once the uplink converter is set up, click “Next”.
3. Downlink data converter.
At the step of adding a downlink converter, you can also select a previously created or create a new downlink converter. But for now, leave the “Downlink data converter” field empty. Click “Skip”.

4. Connection.
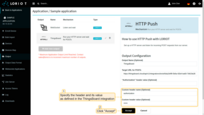
In order for data to be transferred from Loriot to ThingsBoard, you need to configure an Output for your Loriot application. You can do this manually (recommended) or ThingsBoard Integration can do this for you (you will need to specify login and password from your Loriot account for us to be able to automatically provision the output).
We can create the Output by either specifying the “HTTP endpoint URL” of the integration directly in the Loriot account or by enabling the “Create Loriot Application output” option in ThingsBoard and providing your Loriot credentials there.
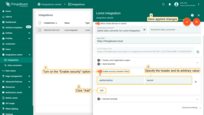
Enable security option
If necessary, you can specify additional parameters, without which the data will not be included in the integration.
To do this, turn on the “Enable security” option. Click “Add” and enter an arbitrary value for the “Header” and “Value” fields. Then, save the changes.
Also need to specify this credentials in Loriot UI.
Once the Headers filter has been configured, it will also need to be specified in the uplink message in the format:
1
-H "$HEADER:$VALUE"
Example:
1
-H "authorization:secret"
Send Uplink message
It may be useful to “emulate” the message from device using console instead of the Loriot server. To send an uplink message, you need a HTTP endpoint URL from the integration.
Use this command to send message. Replace $HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL with corresponding values.
1
curl -v -X POST -d "{\"EUI\":\"BE7A000000000552\",\"data\":\"2A3F\",\"port\":1,\"cmd\":\"rx\",\"dr\":\"SF12 BW125 4/5\",\"snr\":1.2,\"ack\":\"false\",\"freq\":868500000,\"fcnt\":1,\"rssi\":-130,\"ts\":1613745998000}" $HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL -H "Content-Type:application/json"
With the enable security option: replace $HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL and $HEADER:$VALUE with corresponding values.
1
curl -v -X POST -d "{\"EUI\":\"BE7A000000000552\",\"data\":\"2A3F\",\"port\":1,\"cmd\":\"rx\",\"dr\":\"SF12 BW125 4/5\",\"snr\":1.2,\"ack\":\"false\",\"freq\":868500000,\"fcnt\":1,\"rssi\":-130,\"ts\":1613745998000}" $HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL "Content-Type:application/json" -H "$HEADER:$VALUE"
To find the “HTTP endpoint URL”, go to the “Integrations” page in ThingsBoard and click on the Loriot integration to open its details. There, you will find the “HTTP endpoint URL”.
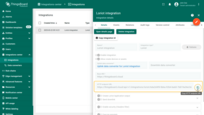
The created device with data can be seen in the ““Devices” page of the “Entities” section.
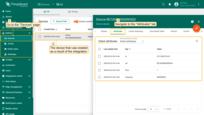
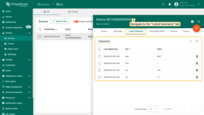
The data can be viewed in the Uplink converter. In the “In”, “Out” and “Metadata” blocks of the “Events” tab:
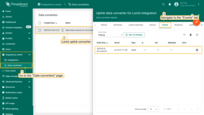
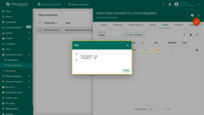
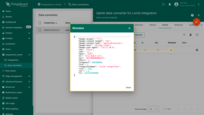
Advanced Usage: Create Downlink Converter
Create Downlink in Data converters. To see events - enable debug mode.
One can use either TBEL (ThingsBoard expression language) or JavaScript to develop user defined functions. We recommend utilizing TBEL as it’s execution in ThingsBoard is much more efficient compared to JS.
You can customize the downlink according to your configuration. Let’s consider an example where we send an attribute update message. So we should change code in the downlink encoder function under
line Also, indicate the required parameters in the metadata: ㅤㅤ*EUI is device EUI and is taken from the device in LORIOT. ㅤㅤ* port can be from 1 to 223. Example for downlink converter:
With this property enabled, the downlink message will be sent to Loriot without double hexadecimal encoding. Example for downlink converter without double hexadecimal encoding: Add a converter to the integration. You can do this at the stage of creating an integration or editing it. |
You can customize the downlink according to your configuration. Let’s consider an example where we send an attribute update message. So we should change code in the downlink encoder function under
line Also, indicate the required parameters in the metadata: ㅤㅤ*EUI is device EUI and is taken from the device in LORIOT. ㅤㅤ* port can be from 1 to 223. Example for downlink converter:
With this property enabled, the downlink message will be sent to Loriot without double hexadecimal encoding. Example for downlink converter without double hexadecimal encoding: Add a converter to the integration. You can do this at the stage of creating an integration or editing it. |
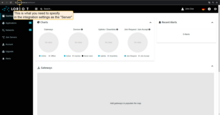
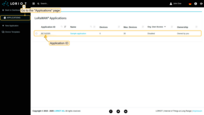
To send Downlink, enable the Send downlink option in the integration. Once we enable the “Send downlink” option, specify the Server, Application ID, Application Access Token in the fields:
To get this data - go to your account in LORIOT.
Data to fill in the Server field:
Data to fill in the Application ID field:
After that, go to Application and go to the Access Tokens section. Find the token that will be specified in the integration.
We can send a message to the device from Rule chain using the rule node. For our example, we create the integration downlink node and set the “Attributes updated” link to it. When changes are made to the attribute, the downlink message will be sent to the integration.
We go to the Device group section in the All folder, to see this with an example. We have indicated the firmware of the device in the Shared attributes. Now we edit it by clicking on the “pencil” icon. Then we make changes to the attribute (change the firmware from 01052020.v1.1 to 01052020.v1.2) and save the data.
Received data and data that was sent can be viewed in the downlink converter.In the “In” block of the Events tab, we see what data entered:
The “Out” field displays messages to device:
It is possible to check that messages have reached LORIOT on the Devices -> LoRaWAN Parameters page at the very bottom in the Downlink Queue field.
Next steps
-
Getting started guides - These guides provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes.
-
Data visualization - These guides contain instructions on how to configure complex ThingsBoard dashboards.
-
Data processing & actions - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Rule Engine.
-
IoT Data analytics - Learn how to use rule engine to perform basic analytics tasks.
-
Advanced features - Learn about advanced ThingsBoard features.